Introduction:
Ethernet is a Link Layer Protocol in the TCP/IP protocol stack between the physical and data link layer. It is the most widely used protocol for Local Area Networks (LANs). Every device on Ethernet is assigned a unique MAC address for communication. Gigabit Ethernet refers to various technologies developed for transmitting Ethernet frames at the rate of gigabits per second. The Reduced Gigabit Media-Independent Interface (RGMII) is used to interface the Ethernet IP core on FPGA with the Gigabit Ethernet PHY chip (RTL8211E) on Mimas A7. The Media Access Layer converts the packets into a stream of data to be sent while the Physical Layer converts the stream of data into electrical signals. RGMII provides a media-independent interface so that MAC and PHY can be compatible, irrespective of the hardware used. In this tutorial, the Numato Lab Mimas A7 FPGA Development Board is used to demonstrate a TCP perf server application which measures downlink performance using LwIp stack. The TCP perf server application runs on lightweight IP (lwIP) stack.
Prerequisites:
-
Hardware:
- TityraCore D200 SODIMM module
- TityraCore Carrier
- Cat 6 Ethernet Cable
- Xilinx Platform Cable USB II JTAG
- USB C-type cable
- 5V DC Power Supply
-
Software:
- Vivado Design Suite 2024.1
- Vitis 2024.2.1
- Serial Terminal (PuTTY, Tera Term, etc.)
- iPerf
Let’s get Started
Step 1:
Download and install Vivado Board Support Package files for Tityra from here.
Step 2:
Open Vivado Design Suite, go to File->Project->New. The New Project window will open. Click Next.
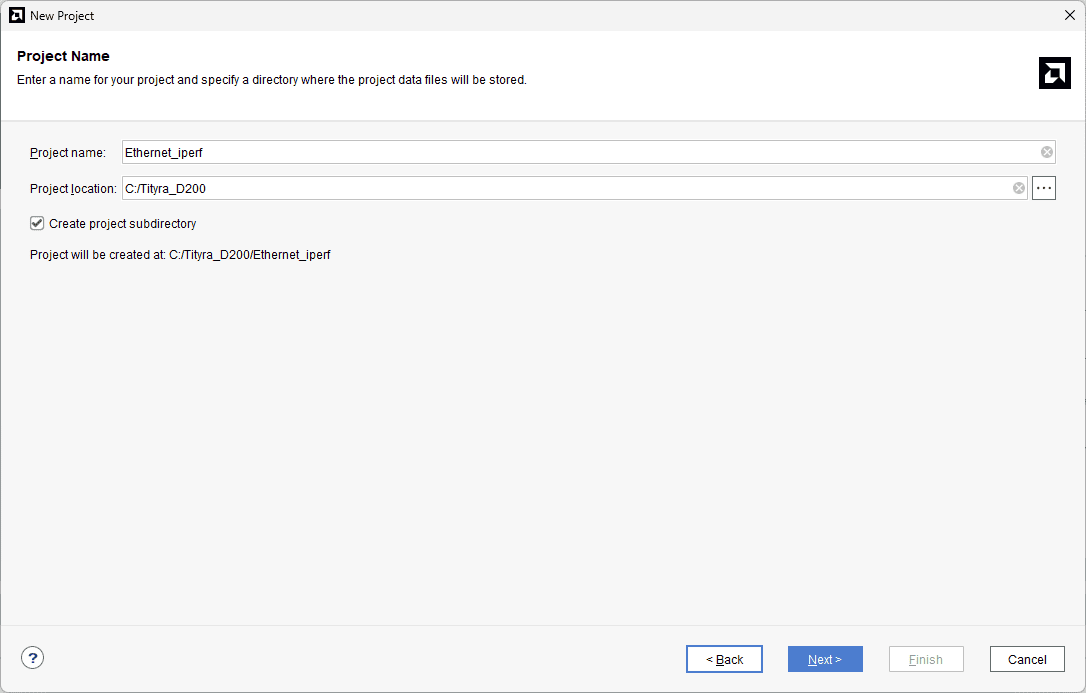
Enter a name for the project and save it at a suitable location. Check the option “Create project subdirectory”. Click Next to continue.
Step 3:
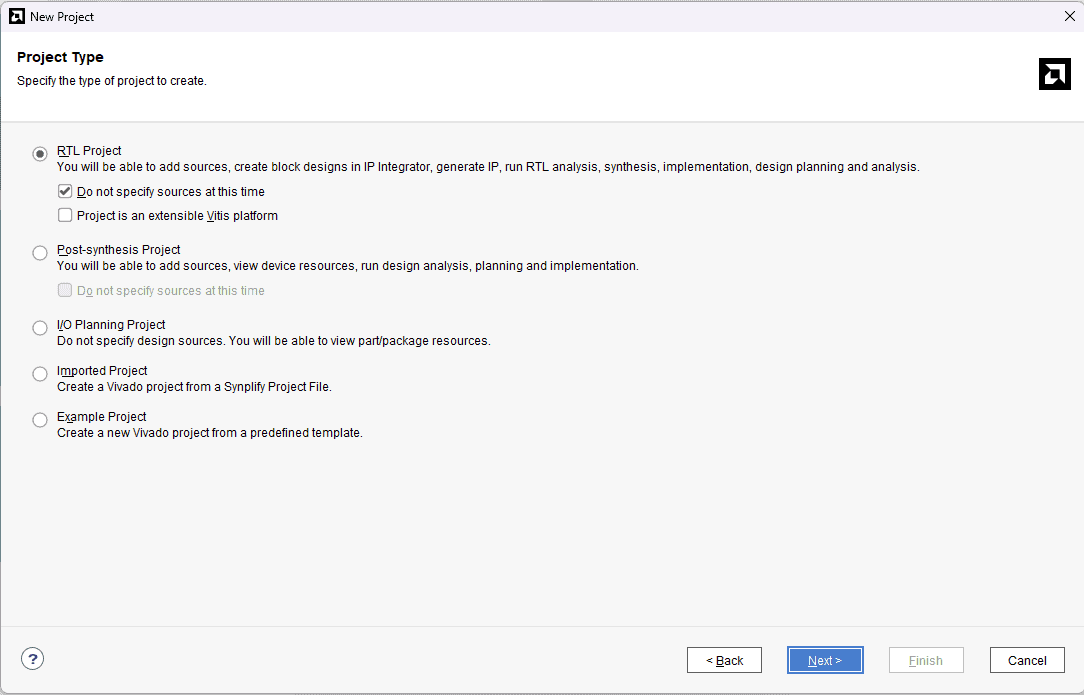
In the Project Type window, select RTL Project and check the “Do not specify sources at this time” option. Click Next.
Step 4:
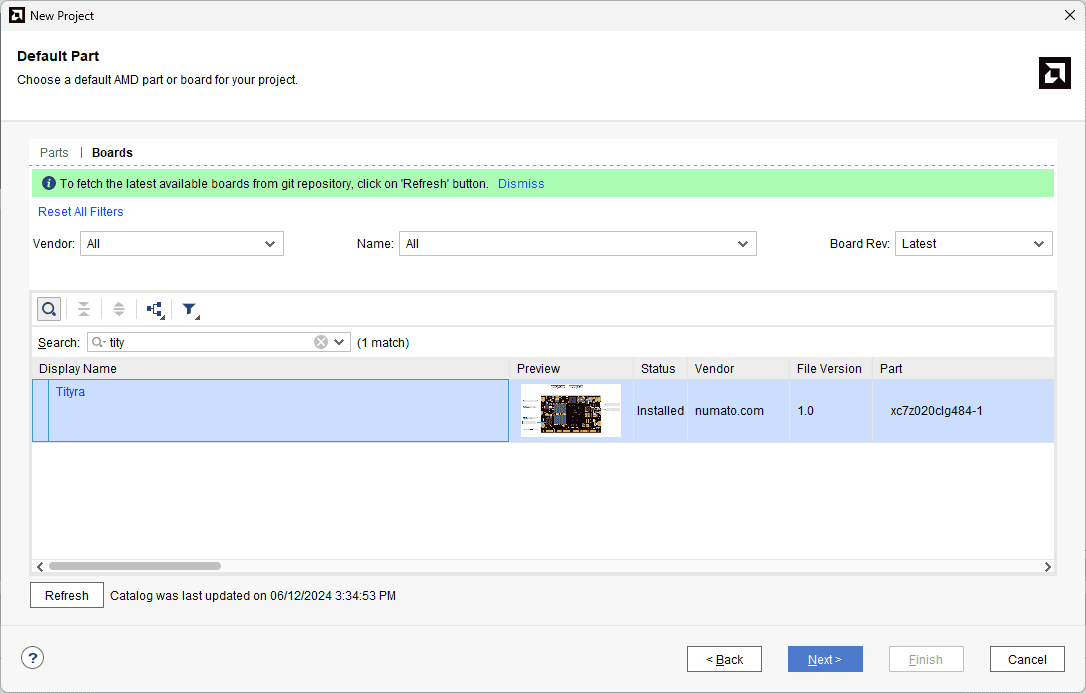
In the Default Part window, select “tityra” from the Boards option. Click Next to continue.
Click Finish to complete creating a new project. Vivado will create a new project with the selected settings.
Step 5:
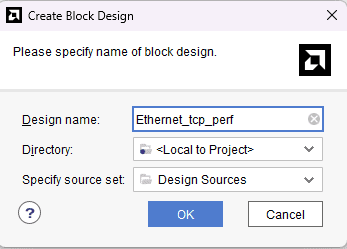
In the Flow Navigator panel, select Create Block Design under IP INTEGRATOR. Enter a name for the block design and click OK. An empty block design will be created
Step 6:
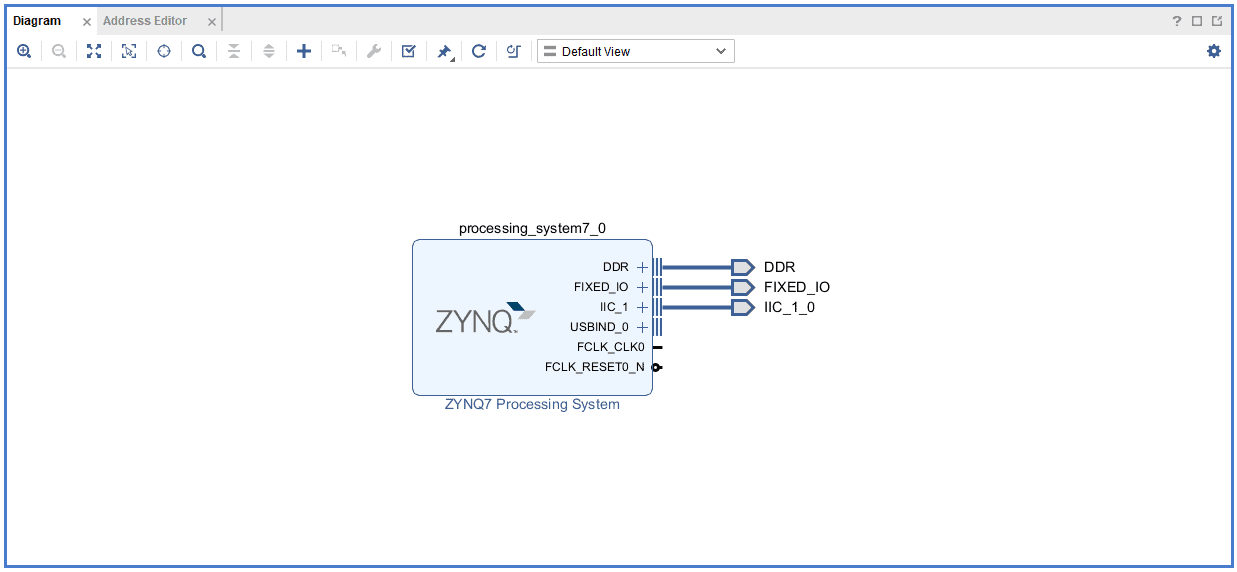
Go to Diagram window, right click and select “Add IP” from the popup menu. Search for ZYNQ7 Processing System. Add it to block design by double clicking.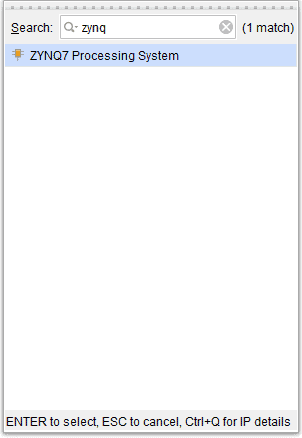
Step 7:
Select “Run Block Automation” in the above right corner of the window and select “ok” in the upcoming window.
Step 8:
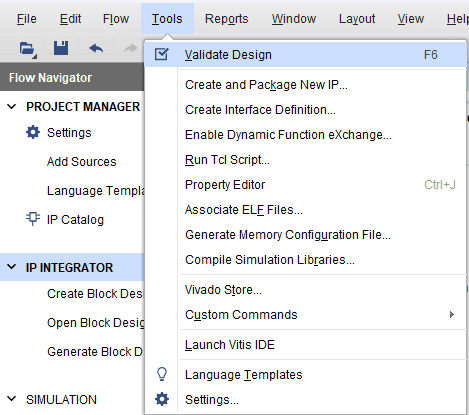
Select the Validate Design option from the Tools menu to ensure that connections are correct.
Step 9:
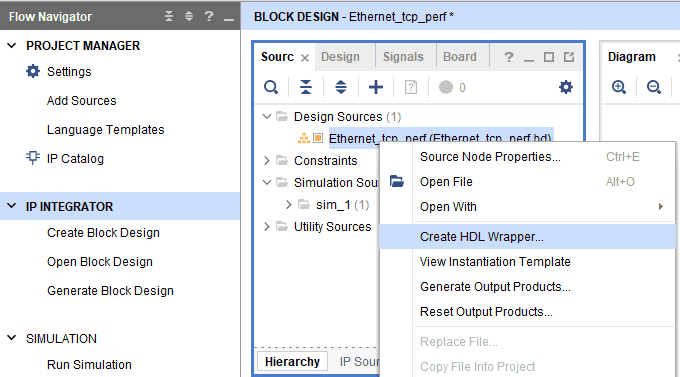
In the Sources window, right-click on the design and select Create HDL Wrapper. Click OK in the dialog box that appears.
Click Generate Bitstream under the PROGRAM AND DEBUG section of Vivado to synthesize, implement and generate the bitstream.
Step 10:
After generating the bitstream successfully, select Export -> Export Hardware from the File menu. Click Next.
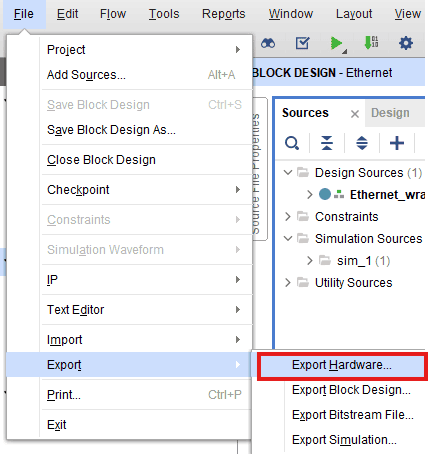
Select the “include bitstream” checkbox and click Next.
Provide the XSA file name and save it at a suitable location. Click Next and click Finish in the next dialog box.
Step 11:
Launch Vitis classic.
Note: In Vivado 2024.1, accessing Vitis via the tools menu inadvertently launches Vitis Unified instead of Vitis Classic, which is our preferred tool for project creation. To utilize Vitis Classic, it is necessary to launch it separately. This differentiation is applicable exclusively to versions released from 2023.2 onwards.
Step 12:
In Vitis, IDE window select Create Application Project and click Next in the dialog box that appears.
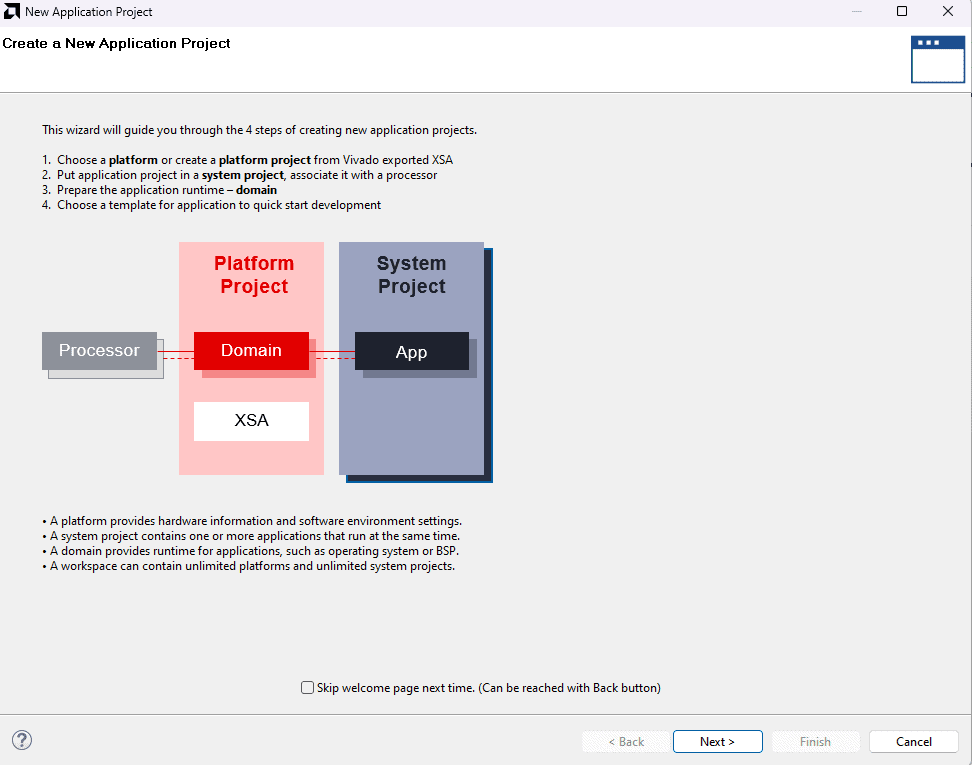
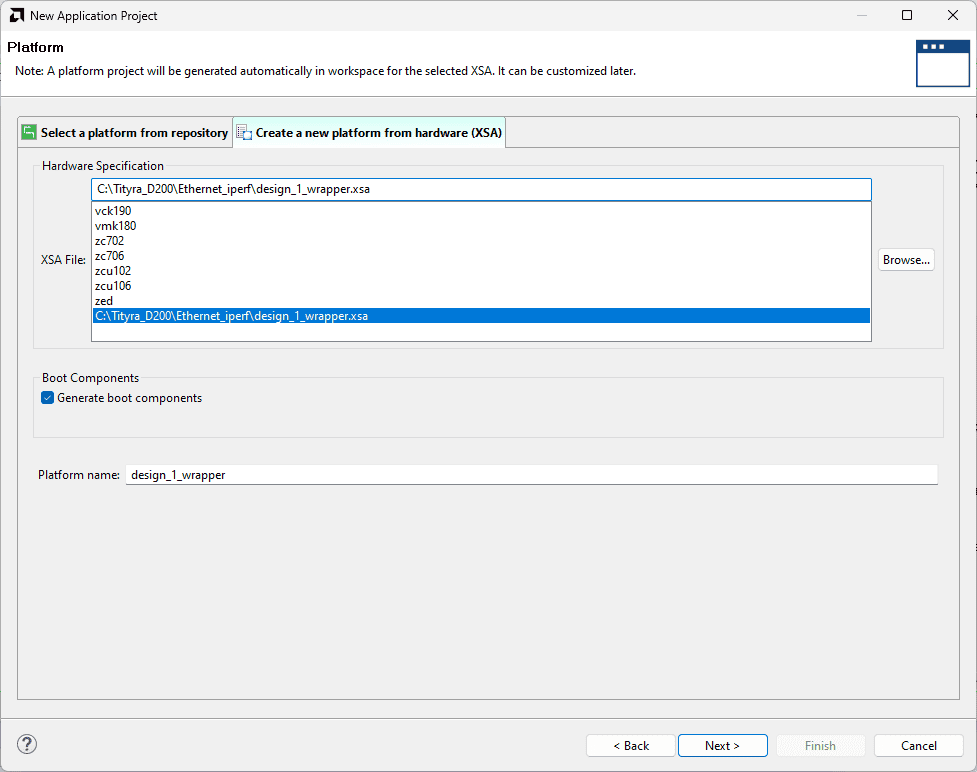
In the Platform, window select Create a new platform from the hardware Tab and import the XSA file which is already created (Provide XSA file location). Click Next.
In the Application Project Details window, give an appropriate name for the Vitis Project and click Next. Click Next in the Domain window.
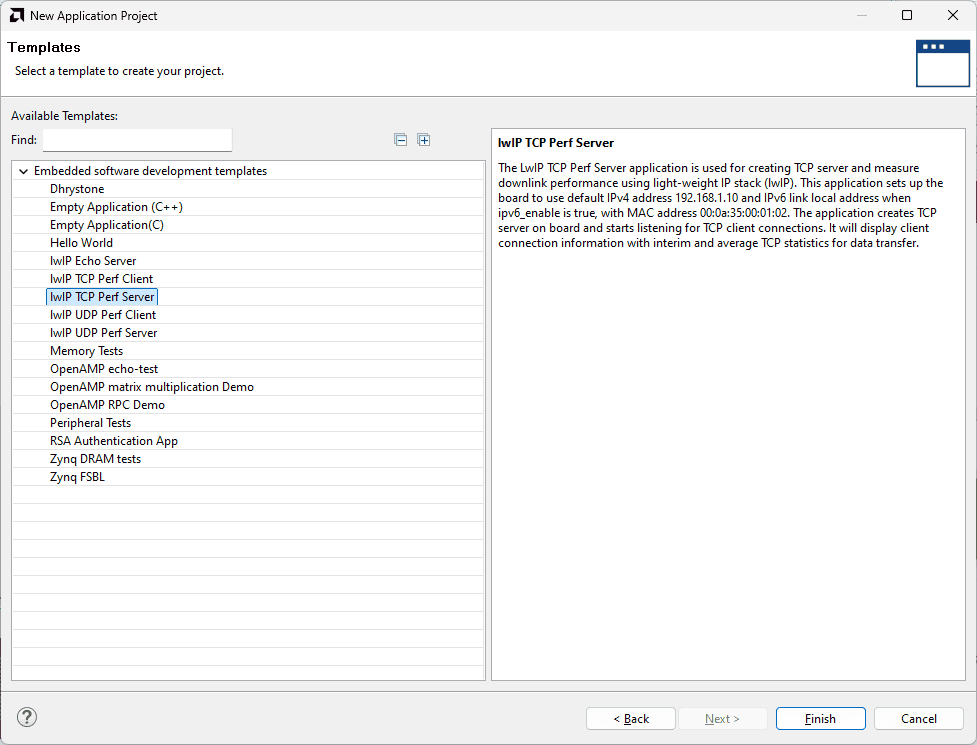
Select the lwIP TCP Perf Server template from the list of available templates and click Finish.
Step 13:
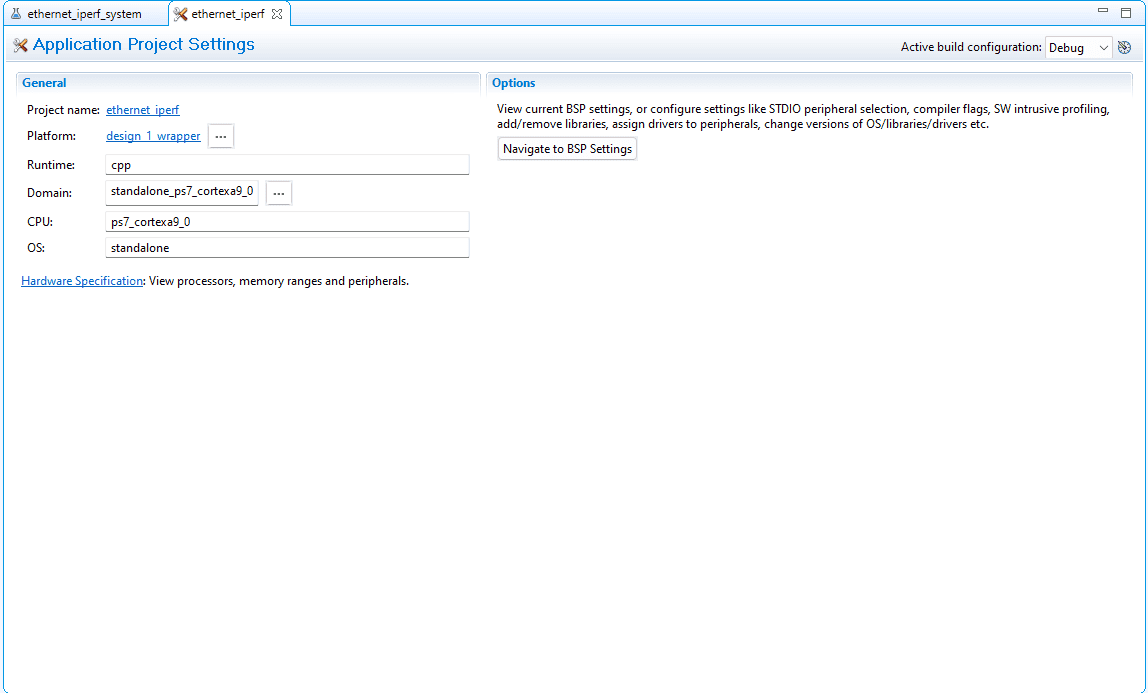
Select Navigate to BSP Settings from Application Project Settings.
Select Board Support Package and click on Modify BSP Settings option.
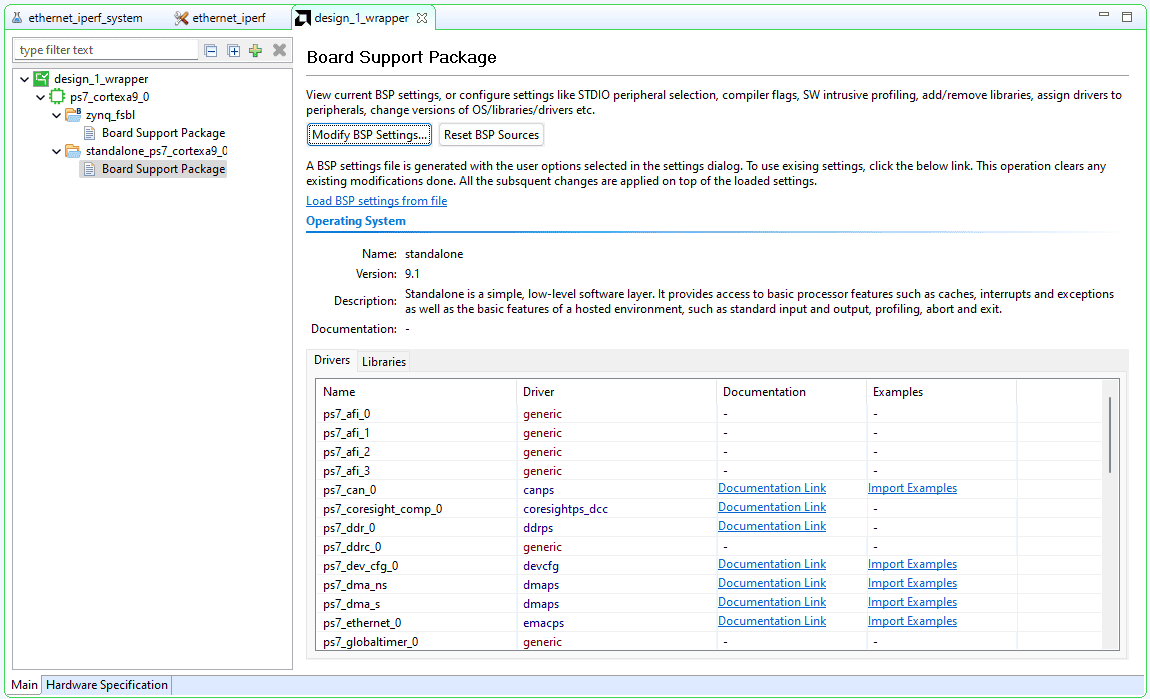
In the Board Support Package Settings window, select lwip (Iwip220) library, change the dhcp_options to “false” and ensure that “debug options” are “false”.
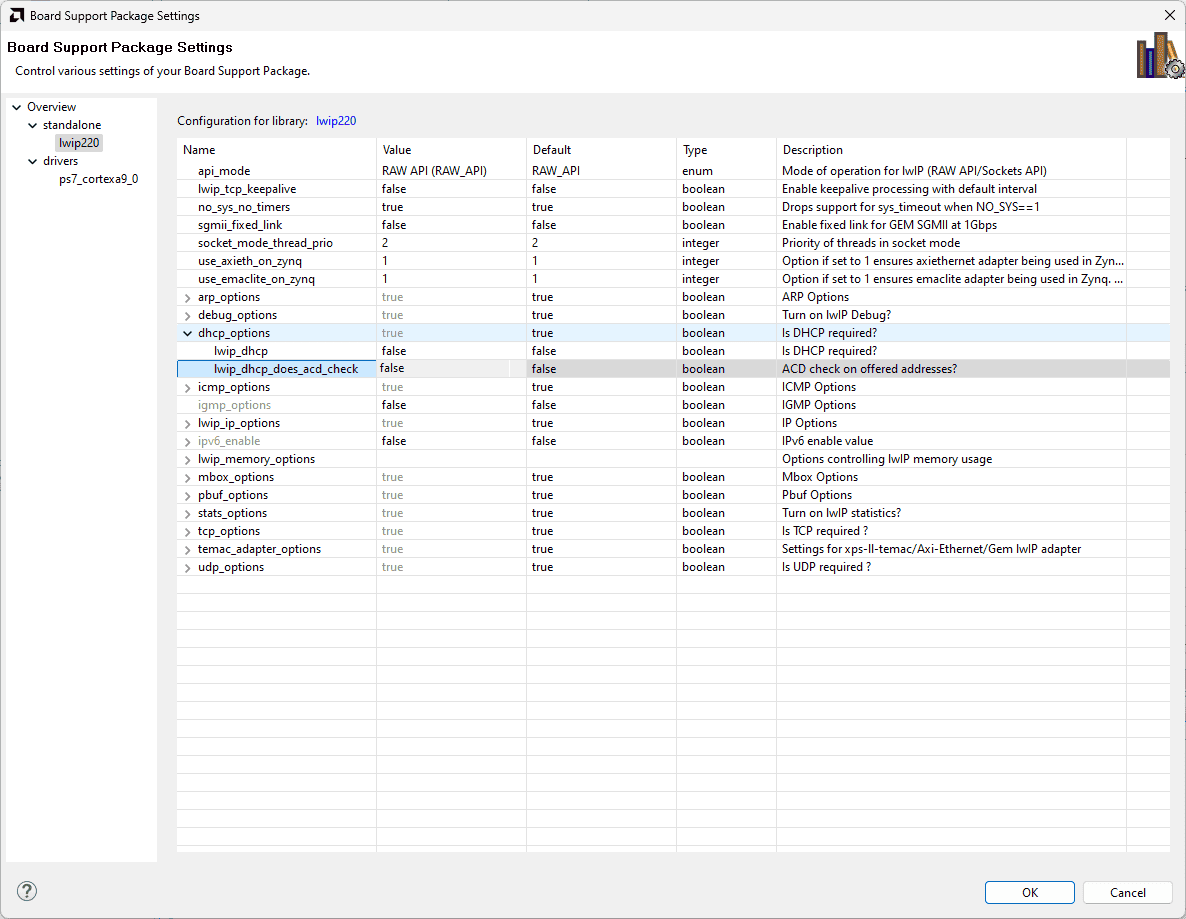
After changing the library settings, click OK. Vitis will update the BSP automatically. If that didn’t happen for any reason, run a build manually.
Step 14:
Once the build is complete successfully, power up TityraCore SODIMM module using carrier and connect Xilinx Platform USB cable and USB type C cable for Serial debugging to the board. Make sure to change the TityraCore’s Boot Mode to JTAG. Please refer to user manual to learn more about configuring Tityra’s Boot Mode.
Step 15:
Program the board by selecting Vitis -> Program Device -> okay. Click Program in the window that opens up.
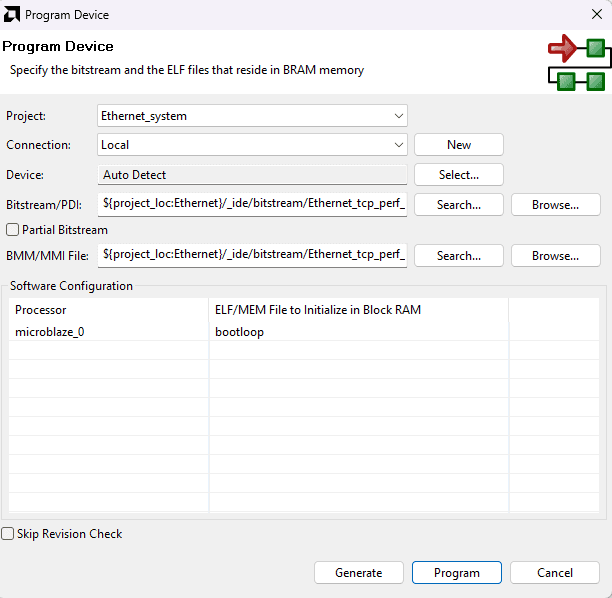
Step 16:
Open any serial terminal program (such as PuTTY, Teraterm etc) and open the port corresponding to TityraCore’s Channel B at 115200 baudrate.
Step 17:
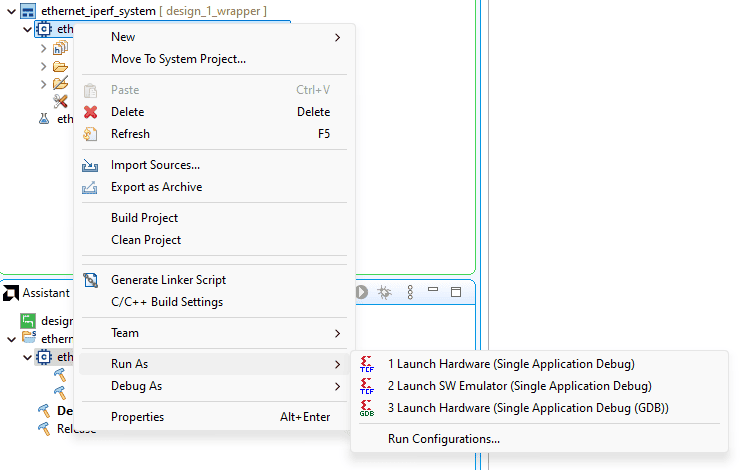
After FPGA is successfully programmed, right click on the executable .elf file of our lwip TCP Perf Server program, go to Run As -> 1 Launch on Hardware (Single Application Debug), as shown in image below:
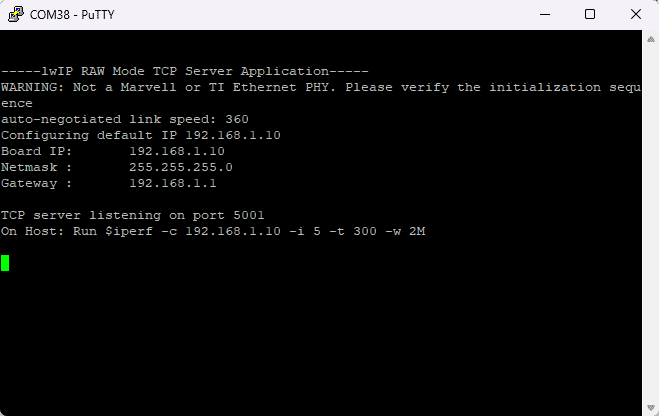
If everything went well, you will see the below output on the Serial Terminal application.
Step 18:
As a part of our network performance testing process, we’ll need to utilize a tool called iPerf. iPerf is a commonly used tool for measuring the maximum TCP and UDP bandwidth performance of a network. Before proceeding, let’s ensure that you have iPerf installed on your system. In this project, we’re utilizing iPerf version 2.0.9 for our network performance testing.
Step 19:
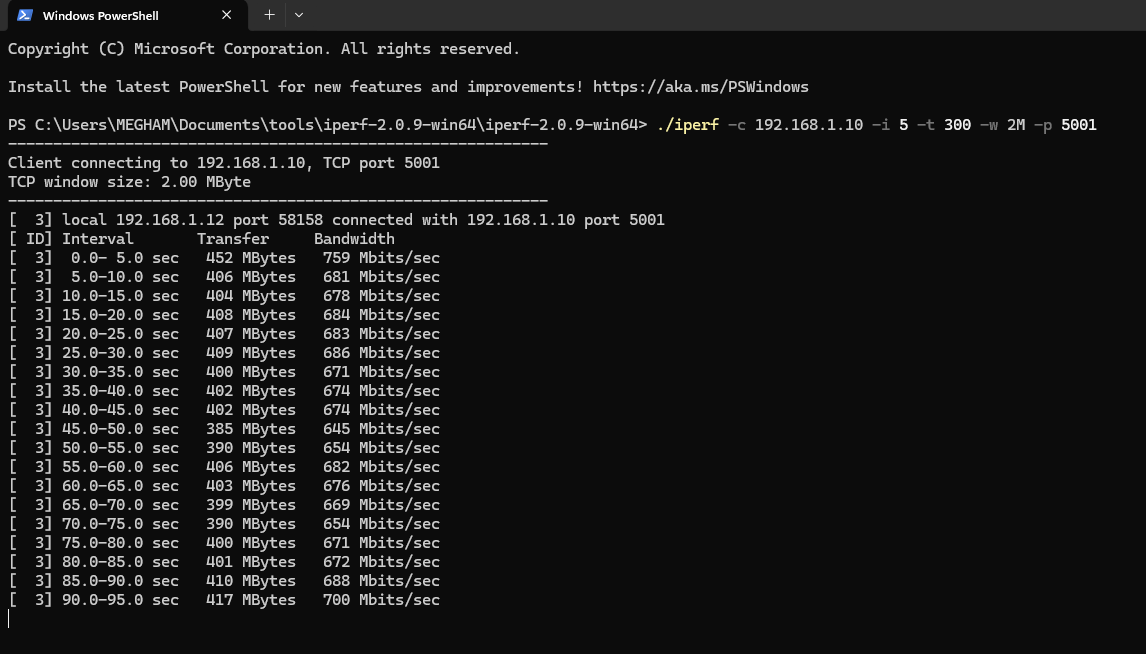
After downloading , Open a command terminal or command prompt and navigate to the directory where iPerf is downloaded.
Enter the command showed in putty ” iperf —c 192.168.1.10 -i 5 —t 300—w 2M -p 5001″ in the command terminal and you can observe the network performance test as shown.
Before proceeding, let’s ensure to Change the IPv4 address of the host system to 192.168.1.15 (any IP address can be used) and the default gateway to 192.168.1.1.