Introduction
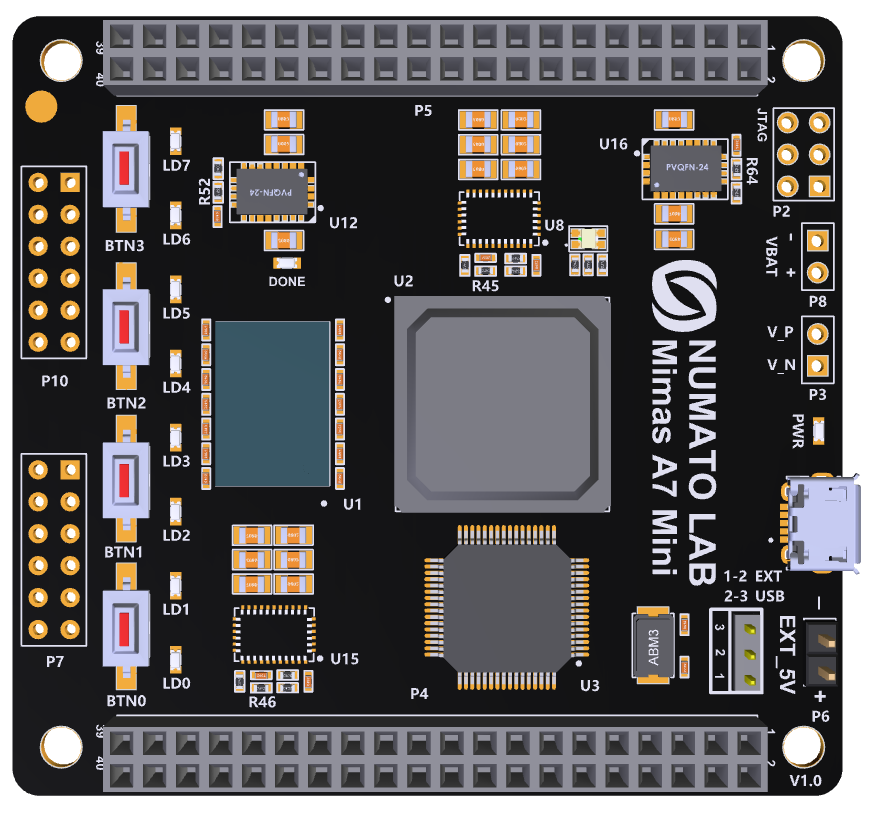
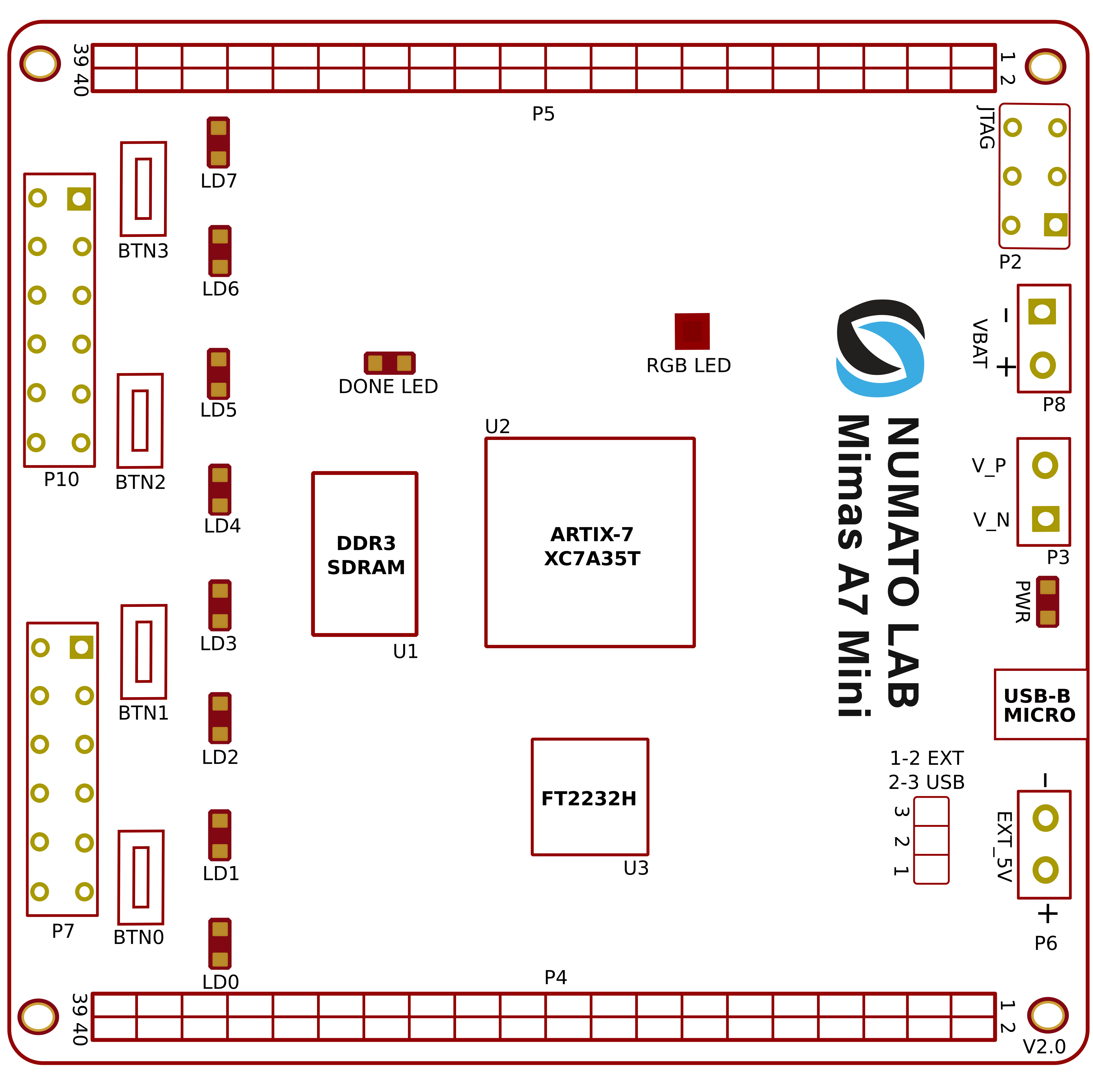
Mimas A7 Mini is an easy to use FPGA Development board featuring Artix 7 FPGA (XC7A35T – FTG256C package) with FTDI’s FT2232H Dual-Channel USB device. It is a Artix-7 based replacement and upgrade of Mimas Spartan 6 FPGA Board. It is specially designed for the development and integration of FPGA based accelerated features to other designs. The USB 2.0 host interface based on popular FT2232H offers high bandwidth data transfer and board programming without the need for any external programming adapters.
Board Features
- Device: Xilinx Artix 7 FPGA (XC7A35T-1FTG256C)
- DDR3: 2Gb DDR3 (MT41J128M16JT-125 or equivalent)
- Onboard 128Mb flash memory for FPGA configuration storage and custom user data storage
- 100MHz CMOS oscillator
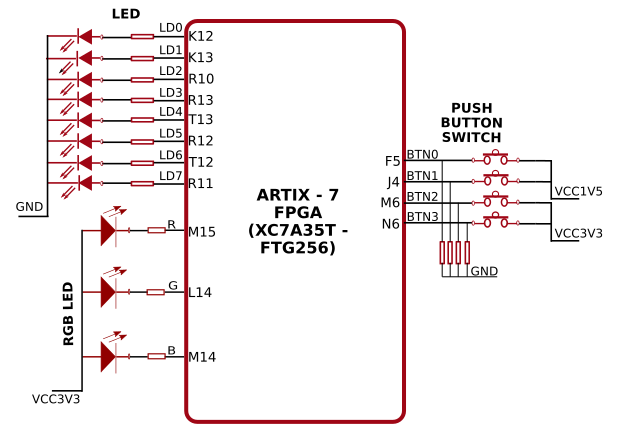
- 8 LEDs, 1 RGB LED and 4 Push Buttons for user-defined purposes
- FPGA configuration via JTAG and USB
- Maximum IOs for user-defined purposes
- FPGA – 70 IOs (35 professionally length matched Differential Pairs) and two 2×6 Expansion Headers
Applications
- Product Prototype Development
- Accelerated computing integration
- Development and testing of custom embedded processors
- Communication devices development
- Educational tool for Schools and Universities
How to use Mimas A7 Mini FPGA Development Board
The following sections describe in detail how to use this module.
Hardware Accessories Required
For easy and fast installation, you may need the following items along with the Mimas A7 Mini module.
- USB C cable / USB A to USB B cable
- DC Power supply
- AMD Platform Cable USB II compatible JTAG programmer
GPIOs
This device is equipped with a maximum of 70 user IO pins that can be used for various custom applications. All user IOs are length matched and can be used as differential pairs.
Header P4
Version 2.0:
| Pin No. On The Header | GPIO Pin Name | Artix-7 (FTG256) Pin No. | Pin No. On The Header | GPIO Pin Name | Artix-7 (FTG256) Pin No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | VCCIO | 1 | GND | ||
| 4 | GPIO_1_P | E12 | 3 | GPIO_1_N | E13 |
| 6 | GPIO_2_P | E16 | 5 | GPIO_2_N | D16 |
| 8 | GPIO_3_P | F15 | 7 | GPIO_3_N | E15 |
| 10 | GPIO_4_P | G14 | 9 | GPIO_4_N | F14 |
| 12 | GPIO_5_P | J15 | 11 | GPIO_5_N | J16 |
| 14 | GPIO_6_P | H14 | 13 | GPIO_6_N | G15 |
| 16 | GPIO_7_P | F12 | 15 | GPIO_7_N | F13 |
| 18 | GPIO_8_P | H12 | 17 | GPIO_8_N | H13 |
| 20 | GPIO_9_P | H11 | 19 | GPIO_9_N | G12 |
| 22 | GPIO_10_P | M5 | 21 | GPIO_10_N | N4 |
| 24 | GPIO_11_P | T4 | 23 | GPIO_11_N | T3 |
| 26 | GPIO_12_P | R3 | 25 | GPIO_12_N | T2 |
| 28 | GPIO_13_P | P4 | 27 | GPIO_13_N | P3 |
| 30 | GPIO_14_P | R2 | 29 | GPIO_14_N | R1 |
| 32 | GPIO_15_P | N3 | 31 | GPIO_15_N | N2 |
| 34 | GPIO_16_P | M2 | 33 | GPIO_16_N | M1 |
| 36 | GPIO_17_P | N1 | 35 | GPIO_17_N | P1 |
| 38 | GPIO_18_P | L4 | 37 | GPIO_18_N | M4 |
| 40 | VCCIO | 39 | GND |
Version 4.0:
| Pin No. On The Header | GPIO Pin Name | Artix-7 (FTG256) Pin No. | Pin No. On The Header | GPIO Pin Name | Artix-7 (FTG256) Pin No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | GND | 1 | VCCIO | ||
| 4 | GPIO_1_P | E12 | 3 | GPIO_1_N | E13 |
| 6 | GPIO_2_P | E16 | 5 | GPIO_2_N | D16 |
| 8 | GPIO_3_P | F15 | 7 | GPIO_3_N | E15 |
| 10 | GPIO_4_P | G14 | 9 | GPIO_4_N | F14 |
| 12 | GPIO_5_P | J15 | 11 | GPIO_5_N | J16 |
| 14 | GPIO_6_P | H14 | 13 | GPIO_6_N | G15 |
| 16 | GPIO_7_P | F12 | 15 | GPIO_7_N | F13 |
| 18 | GPIO_8_P | H12 | 17 | GPIO_8_N | H13 |
| 20 | GPIO_9_P | H11 | 19 | GPIO_9_N | G12 |
| 22 | GPIO_10_P | M5 | 21 | GPIO_10_N | N4 |
| 24 | GPIO_11_P | T4 | 23 | GPIO_11_N | T3 |
| 26 | GPIO_12_P | R3 | 25 | GPIO_12_N | T2 |
| 28 | GPIO_13_P | P4 | 27 | GPIO_13_N | P3 |
| 30 | GPIO_14_P | R2 | 29 | GPIO_14_N | R1 |
| 32 | GPIO_15_P | N3 | 31 | GPIO_15_N | N2 |
| 34 | GPIO_16_P | M2 | 33 | GPIO_16_N | M1 |
| 36 | GPIO_17_P | N1 | 35 | GPIO_17_N | P1 |
| 38 | GPIO_18_P | L4 | 37 | GPIO_18_N | M4 |
| 40 | GND | 39 | VCCIO |
Header P5
Version 2.0:
| Pin No. On The Header | GPIO Pin Name | Artix-7 (FTG256) Pin No. | Pin No. On The Header | GPIO Pin Name | Artix-7 (FTG256) Pin No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | GND | 1 | VCCIO | ||
| 4 | GPIO_19_N | D15 | 3 | GPIO_19_P | D14 |
| 6 | GPIO_20_N | B14 | 5 | GPIO_20_P | C14 |
| 8 | GPIO_21_N | C13 | 7 | GPIO_21_P | D13 |
| 10 | GPIO_22_N | C12 | 9 | GPIO_22_P | C11 |
| 12 | GPIO_23_N | G16 | 11 | GPIO_23_P | H16 |
| 14 | GPIO_35 | G11 | 13 | GPIO_34 | D10 |
| 16 | GPIO_24_N | B16 | 15 | GPIO_24_P | C16 |
| 18 | GPIO_25_N | A15 | 17 | GPIO_25_P | B15 |
| 20 | GPIO_26_N | D11 | 19 | GPIO_26_P | E11 |
| 22 | GND | 21 | GND | ||
| 24 | GPIO_27_N | B11 | 23 | GPIO_27_P | B10 |
| 26 | GPIO_28_N | C9 | 25 | GPIO_28_P | C8 |
| 28 | GPIO_29_N | D9 | 27 | GPIO_29_P | D8 |
| 30 | GPIO_30_N | A14 | 29 | GPIO_30_P | A13 |
| 32 | GPIO_31_N | A12 | 31 | GPIO_31_P | B12 |
| 34 | GPIO_32_N | A10 | 33 | GPIO_32_P | B9 |
| 36 | GPIO_33_N | A9 | 35 | GPIO_33_P | A8 |
| 38 | GPIO_37 | P5 | 37 | GPIO_36 | L5 |
| 40 | GND | 39 | VCCIO |
Version 4.0:
| Pin No. On The Header | GPIO Pin Name | Artix-7 (FTG256) Pin No. | Pin No. On The Header | GPIO Pin Name | Artix-7 (FTG256) Pin No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | VCCIO | 1 | GND | ||
| 4 | GPIO_19_N | D15 | 3 | GPIO_19_P | D14 |
| 6 | GPIO_20_N | B14 | 5 | GPIO_20_P | C14 |
| 8 | GPIO_21_N | C13 | 7 | GPIO_21_P | D13 |
| 10 | GPIO_22_N | C12 | 9 | GPIO_22_P | C11 |
| 12 | GPIO_23_N | G16 | 11 | GPIO_23_P | H16 |
| 14 | GPIO_35 | G11 | 13 | GPIO_34 | D10 |
| 16 | GPIO_24_N | B16 | 15 | GPIO_24_P | C16 |
| 18 | GPIO_25_N | A15 | 17 | GPIO_25_P | B15 |
| 20 | GPIO_26_N | D11 | 19 | GPIO_26_P | E11 |
| 22 | GND | 21 | GND | ||
| 24 | GPIO_27_N | B11 | 23 | GPIO_27_P | B10 |
| 26 | GPIO_28_N | C9 | 25 | GPIO_28_P | C8 |
| 28 | GPIO_29_N | D9 | 27 | GPIO_29_P | D8 |
| 30 | GPIO_30_N | A14 | 29 | GPIO_30_P | A13 |
| 32 | GPIO_31_N | A12 | 31 | GPIO_31_P | B12 |
| 34 | GPIO_32_N | A10 | 33 | GPIO_32_P | B9 |
| 36 | GPIO_33_N | A9 | 35 | GPIO_33_P | A8 |
| 38 | GPIO_37 | P5 | 37 | GPIO_36 | L5 |
| 40 | VCCIO | 39 | GND |
Header P7 (2x6 Expansion Header)
| Pin No. On The Header | GPIO 2X6 CONNECTOR Pin Name | Artix-7 (FTG256) Pin No. | Pin No. On The Header | GPIO 2X6 CONNECTOR Pin Name | Artix-7 (FTG256) Pin No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | VCC | 12 | VCC | ||
| 5 | GND | 11 | GND | ||
| 4 | CONN0_D3 | T10 | 10 | CONN0_D7 | R7 |
| 3 | CONN0_D2 | T9 | 9 | CONN0_D6 | R6 |
| 2 | CONN0_D1 | P11 | 8 | CONN0_D5 | T5 |
| 1 | CONN0_D0 | P10 | 7 | CONN0_D4 | R5 |
Header P10 (2x6 Expansion Header)
| Pin No. On The Header | GPIO 2X6 CONNECTOR Pin Name | Artix-7 (FTG256) Pin No. | Pin No. On The Header | GPIO 2X6 CONNECTOR Pin Name | Artix-7 (FTG256) Pin No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | VCC | 12 | VCC | ||
| 5 | GND | 11 | GND | ||
| 4 | CONN1_D3 | M12 | 10 | CONN1_D7 | R8 |
| 3 | CONN1_D2 | L13 | 9 | CONN1_D6 | P8 |
| 2 | CONN1_D1 | P13 | 8 | CONN1_D5 | P9 |
| 1 | CONN1_D0 | N13 | 7 | CONN1_D4 | N9 |
FT2232H - Artix-7 (FTG256) FPGA Connection Details
| FTDI Pin No. | Pin Function (245 FIFO) | Artix-7 (FTG256) Pin No. |
|---|---|---|
| 16 | FTDI-D0 | M16 |
| 17 | FTDI-D1 | N16 |
| 18 | FTDI-D2 | P15 |
| 19 | FTDI-D3 | P16 |
| 21 | FTDI-D4 | R15 |
| 22 | FTDI-D5 | R16 |
| 23 | FTDI-D6 | T14 |
| 24 | FTDI-D7 | T15 |
| 26 | FTDI-RXE_N | T7 |
| 27 | FTDI-TXE_N | T8 |
| 28 | FTDI-RD_N | N12 |
| 29 | FTDI-WR_N | P14 |
| 33 | FTDI-OE# | L15 |
Driver Installation
Windows
This product requires a driver to be installed for proper functioning when used with Windows. The Numato Lab Mimas A7 Mini driver can be downloaded from here. When the driver installation is complete, the module should appear in FT_Prog Tool as Mimas A7 Mini FPGA Development Board.
Linux
The Linux ships with the drivers required for Mimas A7 Mini. It should be enough to run the following two commands in the terminal:
>> sudo modprobe ftdi_sio >> echo 2a19 100e > /sys/bus/usb-serial/drivers/ftdi_sio/new_id
Generating Bitstream for Mimas A7 Mini
The bitstream can be generated for Mimas A7 Mini in Vivado by following the steps below:
Step 1: It is recommended to generate .bin file along with .bit file. Right-click on “Generate Bitstream” under the “Program and Debug” section of the Flow Navigator window and click “Bitstream Settings”.
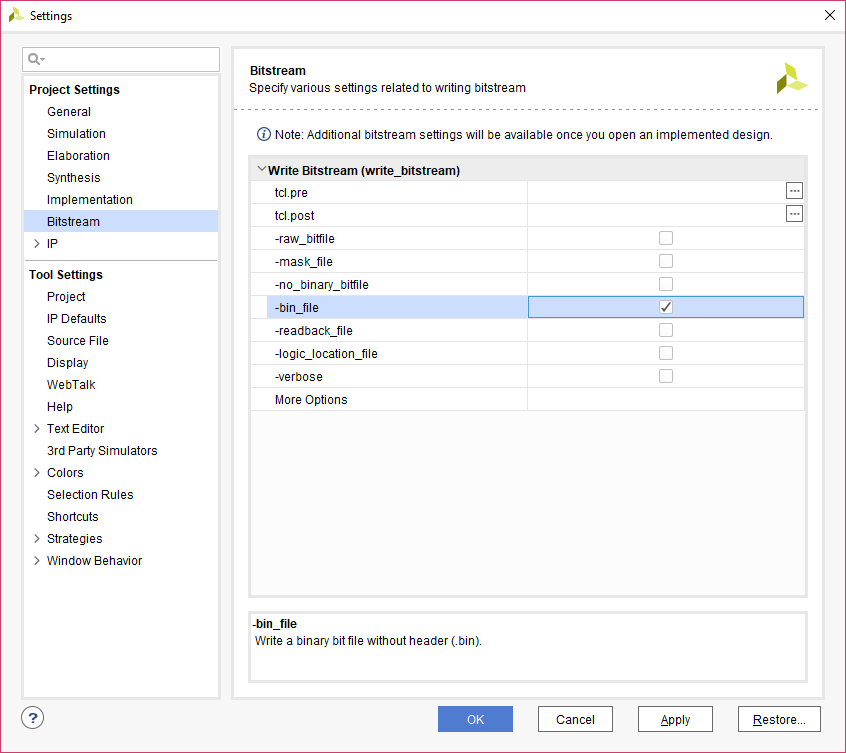
Step 2: Select “-bin_file” option in the dialog window and click “Apply” and then “OK”.
Step 3: Finally click “Generate Bitstream”.
Configuring Mimas A7 Mini Module
Configuring Mimas A7 Mini Module Using JTAG
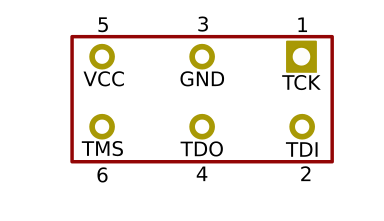
Mimas A7 Mini – Artix-7 Development Board features an onboard JTAG connector that facilitates easy reprogramming of SRAM and onboard SPI flash through JTAG programmer like “Xilinx Platform Cable USB”. Programming Mimas A7 Mini using JTAG requires “Xilinx Vivado Hardware Manager” software which is bundled with Xilinx Vivado Design Suite. To program the SPI flash we need a “.mcs/.bin” file that needs to be generated from the “.bit” file. Steps for generating the “.mcs/.bin” file are as below. Programming FPGA SRAM does not require a “.mcs/.bin” file to be generated.
Generating Memory Configuration File for Mimas A7 Mini using Vivado
The screenshots shown in the following steps are captured from the Vivado Design Suite 2018.2.
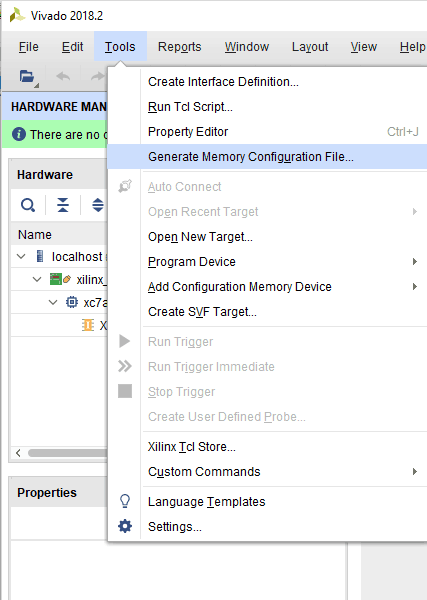
Step 1: Open Xilinx Vivado Hardware Manager. Connect the board, click “Generate Memory Configuration File….” from the “Tools” menu. “Write Memory Configuration File” pop up window will open.
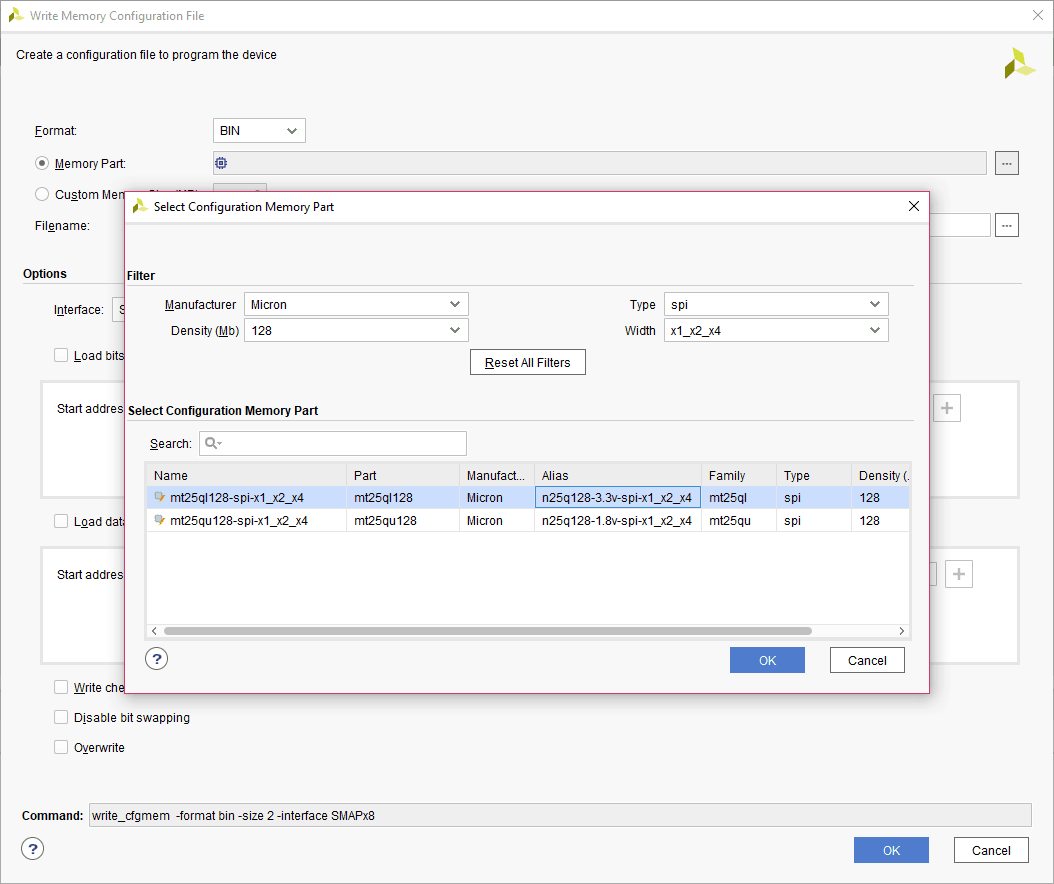
Step 2: Select the ‘Format’ and Configuration Memory Part as shown below. Choose the format as MCS/BIN/HEX depending on your requirement. Now, click “OK”.
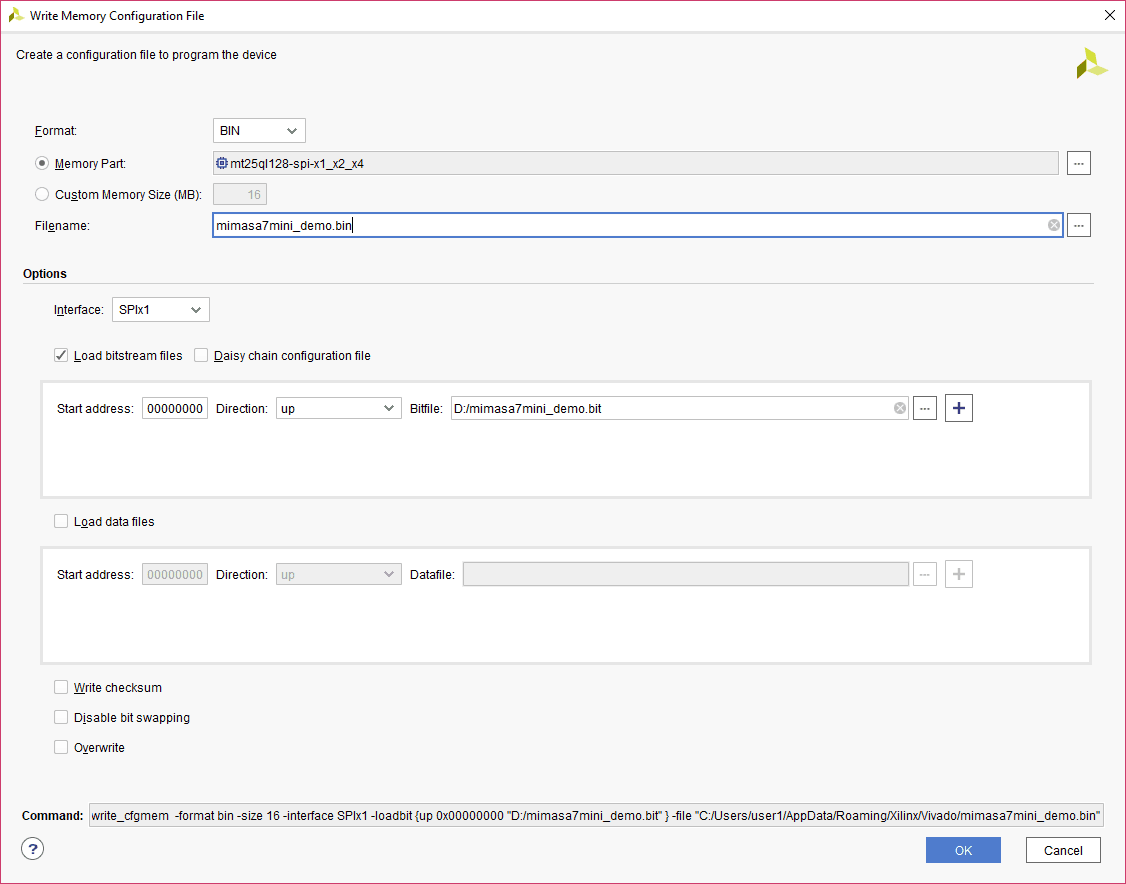
Step 3: Browse to the path where you wish to save the Configuration File and type the file name as “sample.bin” (or any name as per your wish/requirement) to save the memory configuration file (the format of the file may change depending on your “Format”). Select the “Load bitstream files” under the ”Options” tab and browse to the “.bit” file we already generated then click “OK” to generate the memory configuration file.
Programming QSPI Flash using Vivado
A .bin or .mcs file is required for programming Mimas A7 Mini’s onboard QSPI flash.
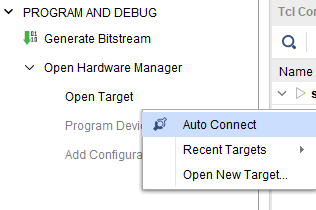
Step 1: Open the Vivado project and open the target by clicking on the “Open Target” in “Open Hardware Manager” in the “Program and Debug” section of the Flow Navigator window. Select “Auto Connect”.
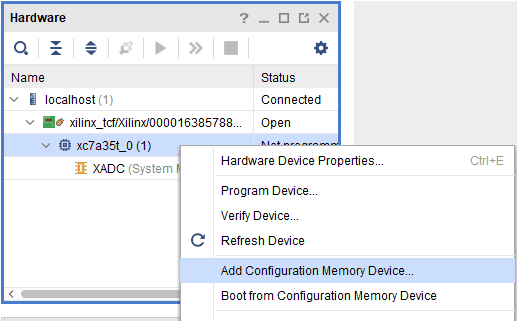
Step 2: If the device is detected successfully, it will be displayed as shown in the image below. To add Configuration Memory Device, right-click on the target device “xc7a35t_0” and select “Add Configuration Memory Device” as shown below.
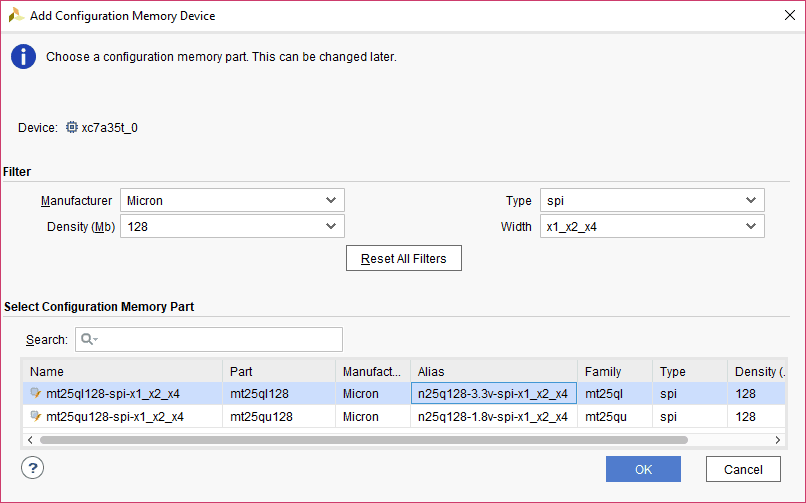
Step 3: Select the memory device “mt25ql128-spi-x1_x2_x4 (which is equivalent to n25q128-3.3v-spi-x1_x2_x4)”, then click OK.
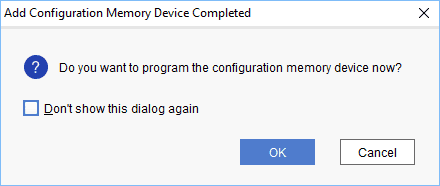
Step 4: After completion of Step 3 the following dialog box will open. Click OK.
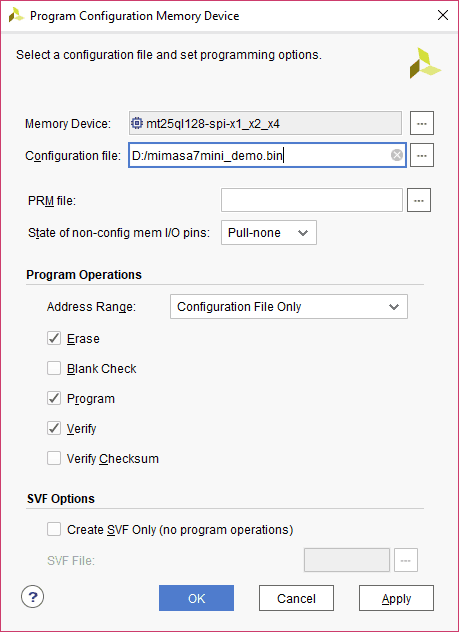
Step 5: Browse to the working .bin file or the .mcs file (whichever applicable) and click OK to program as shown below. If programming is successful, a confirmation message will be displayed.
Programming FPGA using Vivado
Mimas A7 Mini – Artix-7 FPGA Development Board features an onboard JTAG connector that facilitates easy reprogramming of SRAM and onboard SPI flash through JTAG programmer like “Xilinx Platform cable USB”. The following steps illustrate how to program FPGA on Mimas A7 Mini using JTAG.
Step 1: By using JTAG cable, connect Xilinx platform cable USB to Mimas A7 Mini and power it up.
Step 2: Open the Vivado project and open the target by clicking on the “Open Target” in “Open Hardware Manager” in the “Program and Debug” section of the Flow Navigator window. Select “Auto Connect”.
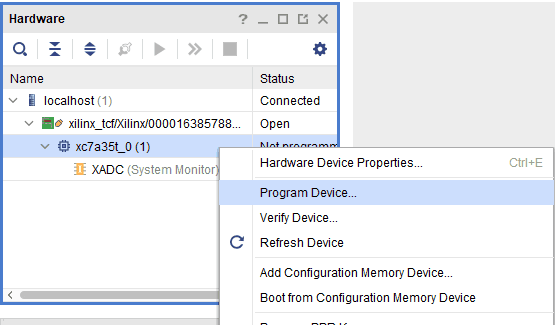
Step 3: If the device is detected successfully, to program the device, right-click on the target device “xc7a35t_0” and select “Program Device” as shown below.
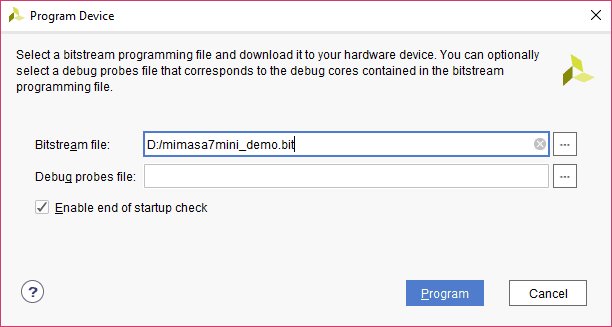
Step 4: In the dialog window which opens up, Vivado automatically chooses the correct bitstream file if the design was synthesized, implemented and if the bitstream was generated successfully. If needed, browse to the bitstream which needs to be programmed to FPGA. Finally, click on “Program”.
Programming Mimas A7 Mini Using Tenagra
For steps on how to program Mimas A7 Mini using Tenagra, refer the Getting started with Tenagra FPGA System Management Software article.
Technical Specifications
| Parameter * | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Specifications | ||
| Number of GPIOs | 70 | |
| On-board oscillator frequency (ASEM1-100.000MHZ-LC-T) | 100 | MHz |
| DDR3 SDRAM (MT41J128M16JT-125 or equivalent) | 2 | Gb |
| Quad SPI Flash Memory (N25Q128A11ESE40FTR) | 128 | Mb |
| Power supply voltage (USB or External) | 5 | V |
| Number of LEDs | 8 | |
| Number of Push Buttons | 4 | |
| FPGA Specifications | ||
| Internal supply voltage relative to GND | -0.5 to 1.1 | V |
| Auxiliary supply voltage relative to GND | -0.5 to 2.0 | V |
| Output drivers supply voltage relative to GND | -0.5 to 3.6 | V |
* All parameters considered nominal. Numato Systems Pvt Ltd reserves the right to modify products without notice.
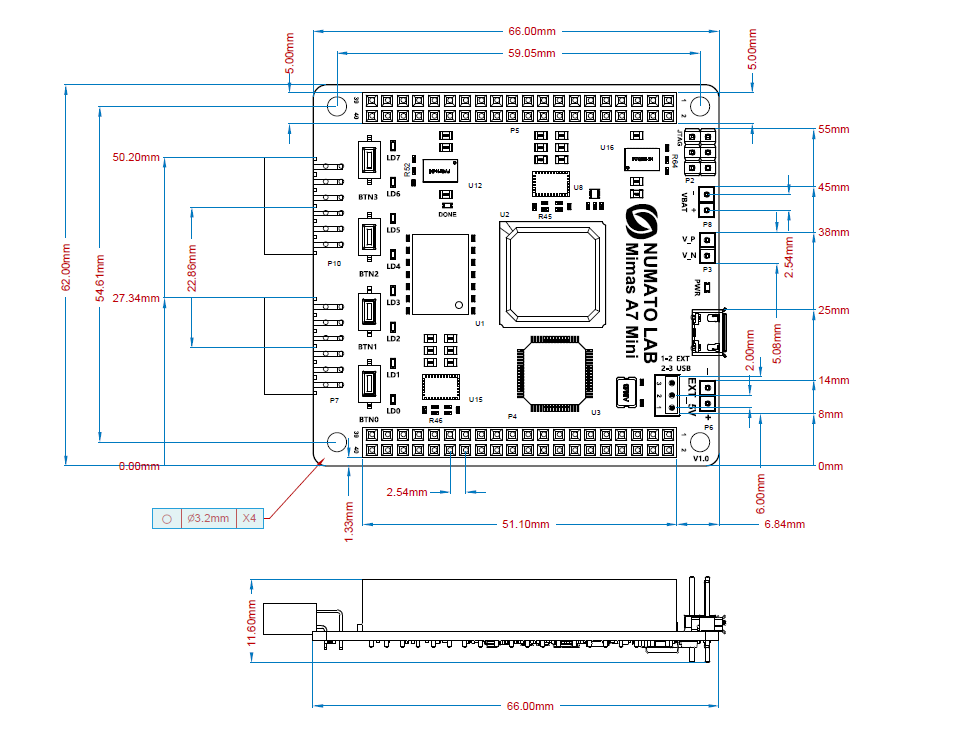
Mimas A7 Mini GPIO Easy Reference
Version 2.0: Mimas A7 Mini GPIO Easy Reference
Version 4.0: Mimas A7 Mini GPIO Easy Reference