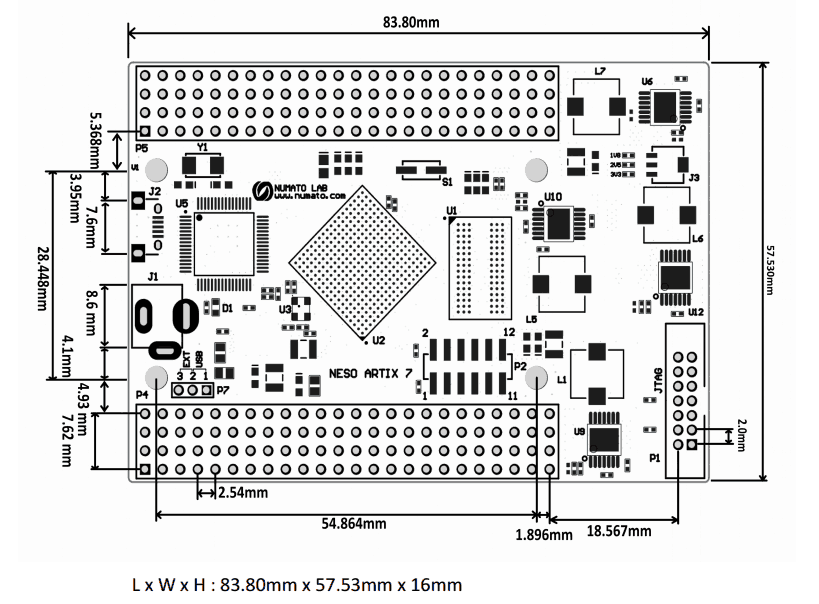
Introduction
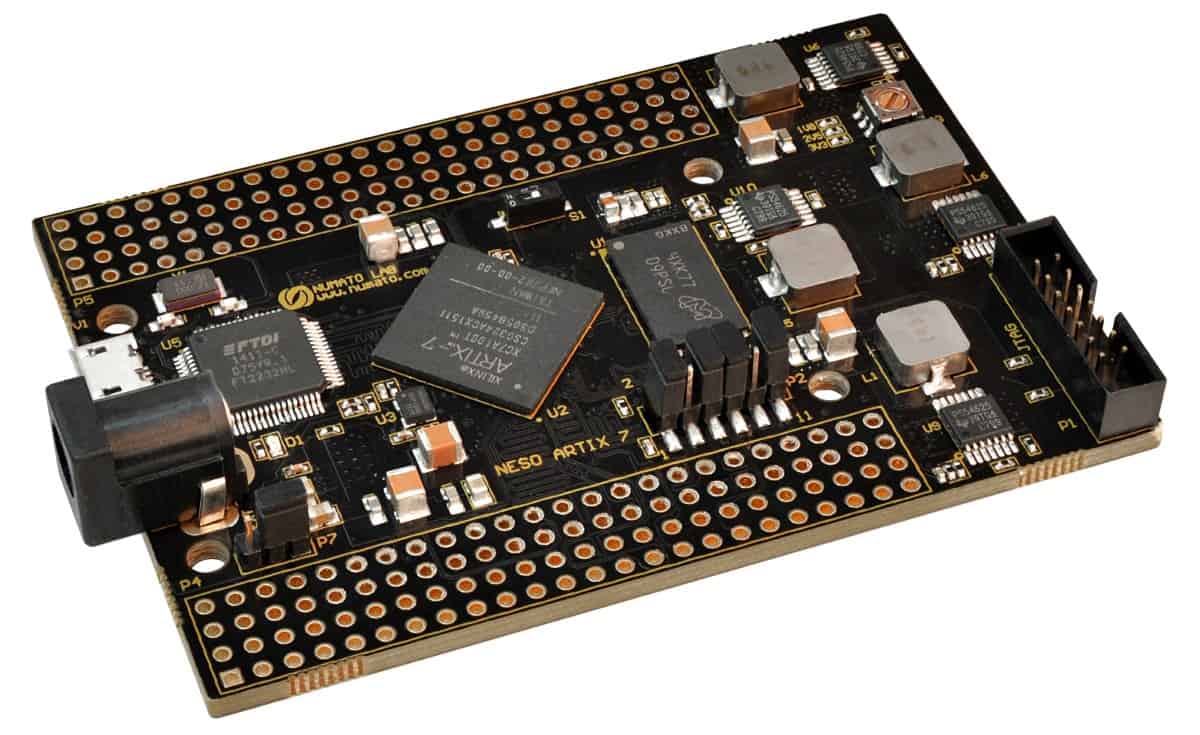
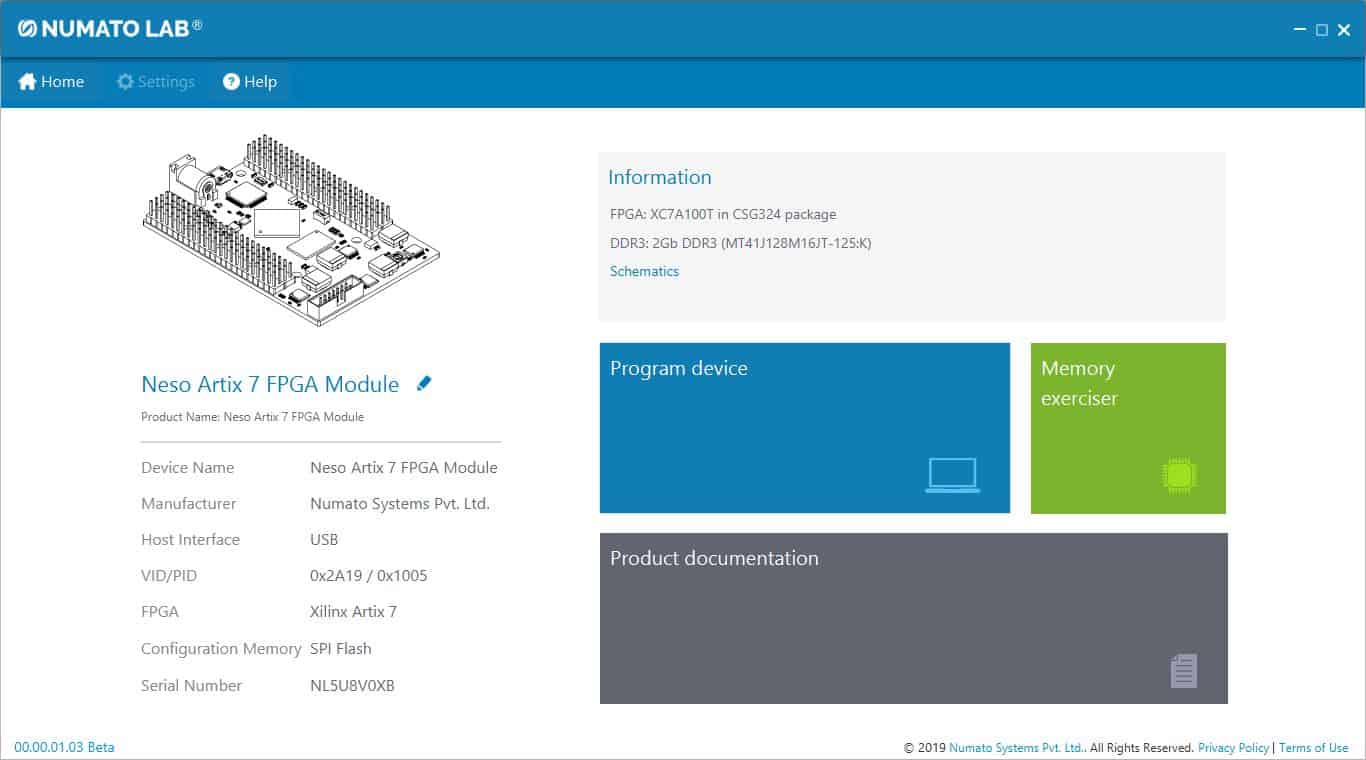
Neso is an easy to use FPGA Development board featuring Artix 7 FPGA. It is specially designed for the development and integration of FPGA based accelerated features to other designs. This development board features Xilinx XC7A100T FPGA with FTDI’s FT2232H Dual-Channel USB device. The high-speed USB 2.0 interface provides fast and easy configuration download to the on-board SPI flash. No programmer or special downloader cable is needed to download the bitstream to the board.
Applications
- Product Prototype Development
- Accelerated computing integration
- Development and testing of custom embedded processors
- Signal Processing
- Communication devices development
- Educational tool for Schools and Universities
Board features
- FPGA: XC7A100T in CSG324 package
- DDR3: 2Gb DDR3 (MT41J128M16JT-125:K)
- Flash memory: 128 Mb SPI flash memory (N25Q128A13ESE40E)
- 100MHz CMOS oscillator
- High-Speed USB 2.0 interface for On-board flash programming.
Revision V1: FT2232H Channel A is dedicated to SPI Flash /JTAG Programming. Channel B can be used for custom applications.
Revision V2: FT2232H Channel B is dedicated to SPI Flash /JTAG Programming. Channel A can be used for custom applications. - On-board voltage regulators for single power rail operation
- FPGA configuration via JTAG and USB
- Maximum IOs for user-defined purposes FPGA – 140 IOs FT2232H – 8 IOs
How to Use NESO Artix 7 FPGA Development Board
Components/Tools Required
Along with the module, you may need the items in the list below for easy and fast installation.
1. USB A to Micro B cable.
2. DC Power supply (Optional).
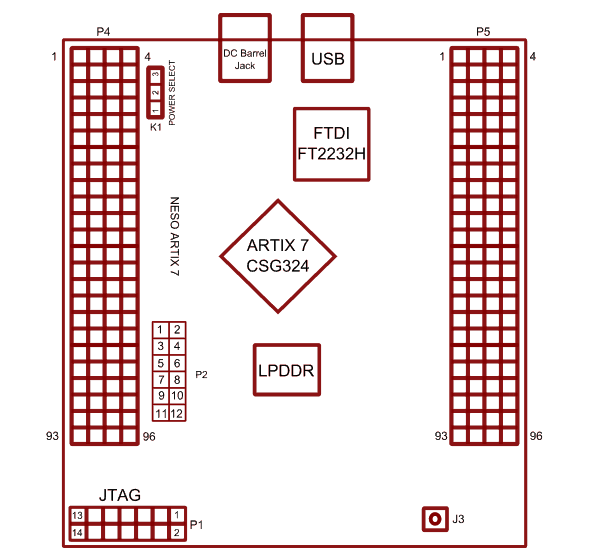
USB Interface
 The onboard full-speed USB controller helps a Windows/Linux/Mac computer to communicate with this module. Use a USB A to Micro B cable to connect with a PC. By default, the module is powered from USB so make sure not to overcrowd unpowered USB hubs (the picture on the right shows USB Micro connector).
The onboard full-speed USB controller helps a Windows/Linux/Mac computer to communicate with this module. Use a USB A to Micro B cable to connect with a PC. By default, the module is powered from USB so make sure not to overcrowd unpowered USB hubs (the picture on the right shows USB Micro connector).
Note: In the revision V1 of Neso, FT2232H Channel A is dedicated to SPI Flash /JTAG Programming. Channel B can be used for custom applications. The revision V2 of Neso ships with FT2232H Channel B dedicated for SPI Flash /JTAG Programming whereas Channel A can be used for custom applications.
DC Power Supply
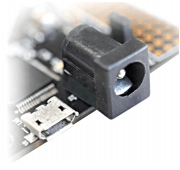 This module uses a +5V power supply to function properly. By default, the board is configured to use the +5V supply from USB. So an external +5V power is not required unless the USB port is unable to supply enough current. In most cases, USB ports are capable of providing enough current for the module. The current requirement for this board largely depends on your application. Please consult the FPGA datasheet for more details on power requirements. If for any reason, an external 5V power supply needs to be used for the module, the Power select jumper should be configured properly before connecting the power supply. Please refer to the marking on the board for more details.
This module uses a +5V power supply to function properly. By default, the board is configured to use the +5V supply from USB. So an external +5V power is not required unless the USB port is unable to supply enough current. In most cases, USB ports are capable of providing enough current for the module. The current requirement for this board largely depends on your application. Please consult the FPGA datasheet for more details on power requirements. If for any reason, an external 5V power supply needs to be used for the module, the Power select jumper should be configured properly before connecting the power supply. Please refer to the marking on the board for more details.
Power Select
The Power Select header K1 is used to configure the power source for the board. Connect pins 1 and 2 to use USB power and connect pins 2 and 3 to use the external DC power.
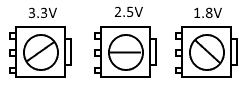
VADJ Supply
This board is equipped with a rotary switch (J3) for selecting a bank 35 IO voltage level. It is possible to select 3 different voltage levels for the bank ie, 1.8V, 2.5V and 3.3V as per the user requirement. Possible rotary switch positions and the resultant VADJ voltages are illustrated below:
JTAG/SPI Jumper Configuration on FT2232H Configuration Channel
The configuration channel of FT2232H in Neso can be connected to the SPI bus that connects the SPI Flash chip to the FPGA or to the JTAG pins of the FPGA. By connecting SPI bus to FT2232H, the SPI flash can be directly programmed to save the configuration permanently (non-volatile, until erased). This is the default configuration set when Neso is shipped. In the revision V1 of Neso, FT2232H Channel A is the configuration channel and is dedicated to SPI Flash /JTAG Programming. Channel B can be used for custom applications. The revision V2 of Neso ships with FT2232H Channel B is the configuration channel and is dedicated to SPI Flash /JTAG Programming whereas Channel A can be used for custom applications.
When the FT2232H configuration channel is connected to SPI, Neso Configuration Downloader utility can be used to program the board. When the FT2232H configuration channel is connected to FPGA JTAG, the JTAG signals can be accessed directly through FT2232H. Neso Configuration Downloader utility currently does not support programming FPGA SRAM through JTAG.
Please see the tables below for information about selecting SPI or JTAG for the FT2232H configuration channel. SPI must be selected for Neso Configuration Downloader utility to work.
Header P10
| Jumper Configuration for SPI | Jumper Configuration for JTAG |
|---|---|
| 1 - 2 | 2 - 4 |
| 5 - 6 | 3 - 5 |
| 7 - 8 | 8 - 10 |
| 11 - 12 | 9 - 11 |
Important: These jumper settings are only meant for accessing the JTAG signals via FT2232H through USB using programs such as xc3sprog. If you are using external JTAG such as Xilinx Platform Cable USB II connected to the JTAG header, then please do not change these jumpers. They should be in the factory-shipped SPI configuration. If the jumpers are changed to JTAG mode, and an external JTAG is used, then the external JTAG will not work.
GPIOs
This device is equipped with a maximum of 140 user IO pins that can be used for various custom applications. All user IOs are length matched and can be used as differential pairs.
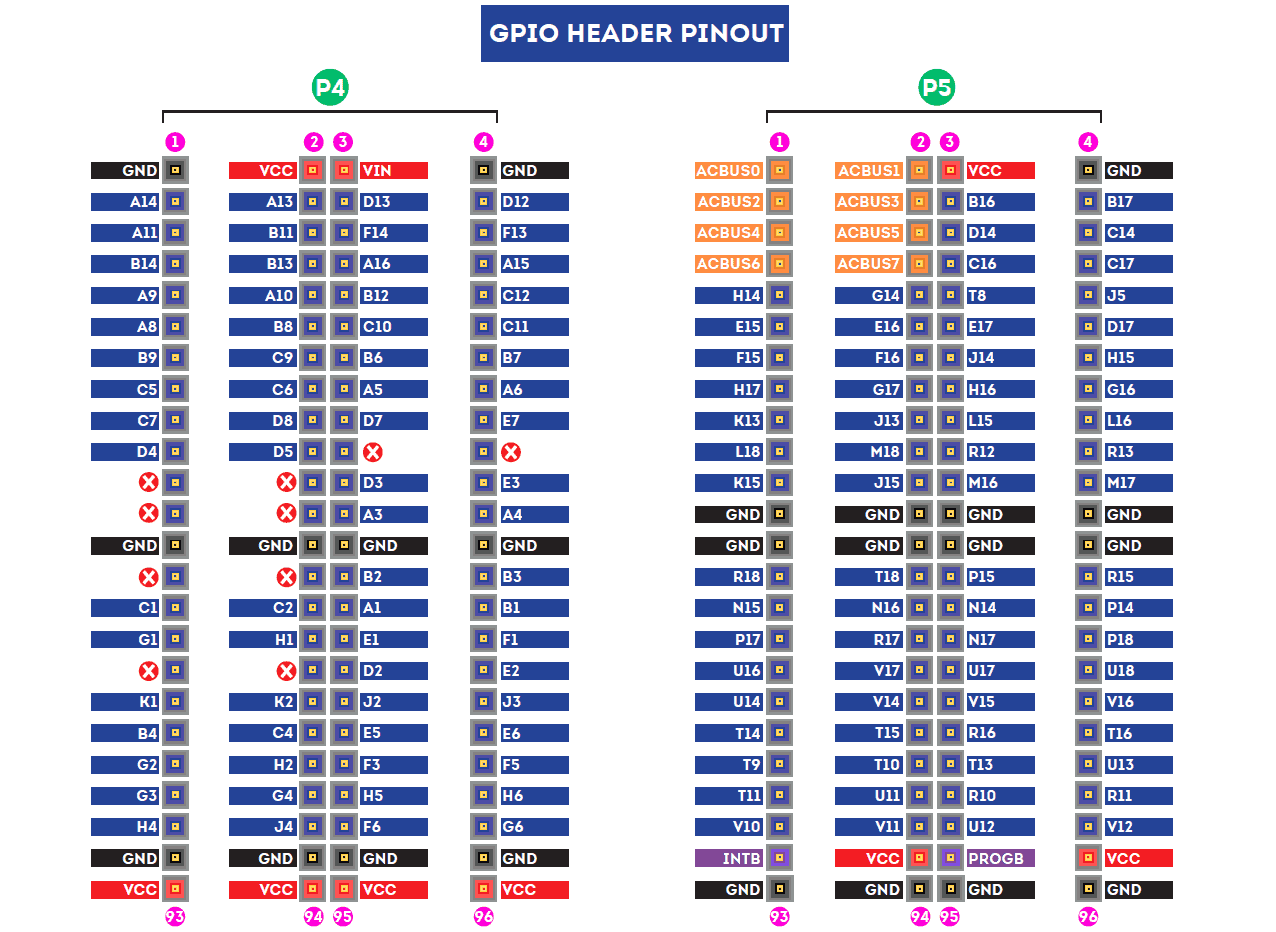
Neso Revision V1:
Header P4
| Pin No. On The Header | Artix-7 (CSG324) Pin No. | Pin No. On The Header | Artix-7 (CSG324) Pin No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | 2 | 3V3 |
| 3 | VCCIN | 4 | GND |
| 5 | A14 | 6 | A13 |
| 7 | D13 | 8 | D12 |
| 9 | A11 | 10 | B11 |
| 11 | F14 | 12 | F13 |
| 13 | B14 | 14 | B13 |
| 15 | A16 | 16 | A15 |
| 17 | A9 | 18 | A10 |
| 19 | B12 | 20 | C12 |
| 21 | A8 | 22 | B8 |
| 23 | C10 | 24 | C11 |
| 25 | B9 | 26 | C9 |
| 27 | B6 | 28 | B7 |
| 29 | C5 | 30 | C6 |
| 31 | A5 | 32 | A6 |
| 33 | C7 | 34 | D8 |
| 35 | D7 | 36 | E7 |
| 37 | D4 | 38 | D5 |
| 39 | - | 40 | - |
| 41 | - | 42 | - |
| 43 | D3 | 44 | E3 |
| 45 | - | 46 | - |
| 47 | A3 | 48 | A4 |
| 49 | GND | 50 | GND |
| 51 | GND | 52 | GND |
| 53 | - | 54 | - |
| 55 | B2 | 56 | B3 |
| 57 | C1 | 58 | C2 |
| 59 | A1 | 60 | B1 |
| 61 | G1 | 62 | H1 |
| 63 | E1 | 64 | F1 |
| 65 | - | 66 | - |
| 67 | D2 | 68 | E2 |
| 69 | K1 | 70 | K2 |
| 71 | J2 | 72 | J3 |
| 73 | B4 | 74 | C4 |
| 75 | E5 | 76 | E6 |
| 77 | G2 | 78 | H2 |
| 79 | F3 | 80 | F5 |
| 81 | G3 | 82 | G4 |
| 83 | H5 | 84 | H6 |
| 85 | H4 | 86 | J4 |
| 87 | F6 | 88 | G6 |
| 89 | GND | 90 | GND |
| 91 | GND | 92 | GND |
| 93 | 3V3 | 94 | 3V3 |
| 95 | 3V3 | 96 | 3V3 |
Header P5
| Pin No. On The Header | Artix-7 (CSG324) Pin No. | Pin No. On The Header | Artix-7 (CSG324) Pin No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ACBUS0* | 2 | ACBUS1 |
| 3 | 3V3 | 4 | GND |
| 5 | ACBUS2 | 6 | ACBUS3 |
| 7 | B16 | 8 | B17 |
| 9 | ACBUS4 | 10 | ACBUS5 |
| 11 | D14 | 12 | C14 |
| 13 | ACBUS6 | 14 | ACBUS7 |
| 15 | C16 | 16 | C17 |
| 17 | H14 | 18 | G14 |
| 19 | D15 | 20 | C15 |
| 21 | E15 | 22 | E16 |
| 23 | E17 | 24 | D17 |
| 25 | F15 | 26 | F16 |
| 27 | J14 | 28 | H15 |
| 29 | H17 | 30 | G17 |
| 31 | H16 | 32 | G16 |
| 33 | K13 | 34 | J13 |
| 35 | L15 | 36 | L16 |
| 37 | L18 | 38 | M18 |
| 39 | R12 | 40 | R13 |
| 41 | K15 | 42 | J15 |
| 43 | M16 | 44 | M17 |
| 45 | GND | 46 | GND |
| 47 | GND | 48 | GND |
| 49 | GND | 50 | GND |
| 51 | GND | 52 | GND |
| 53 | R18 | 54 | T18 |
| 55 | P15 | 56 | R15 |
| 57 | N15 | 58 | N16 |
| 59 | N14 | 60 | P14 |
| 61 | P17 | 62 | R17 |
| 63 | N17 | 64 | P18 |
| 65 | U16 | 66 | V17 |
| 67 | U17 | 68 | U18 |
| 69 | U14 | 70 | V14 |
| 71 | V15 | 72 | V16 |
| 73 | T14 | 74 | T15 |
| 75 | R16 | 76 | T16 |
| 77 | T9 | 78 | T10 |
| 79 | T13 | 80 | U13 |
| 81 | T11 | 82 | U11 |
| 83 | R10 | 84 | R11 |
| 85 | V10 | 86 | V11 |
| 87 | U12 | 88 | V12 |
| 89 | INITB | 90 | 3V3 |
| 91 | PROGB | 92 | 3V3 |
| 93 | GND | 94 | GND |
| 95 | GND | 96 | GND |
FT2232H – Artix-7 (CSG324) FPGA Connection Details
| FTDI Pin No. | Pin Function (245 FIFO) | Artix-7 Pin No. |
|---|---|---|
| 38 | D0 | A18 |
| 39 | D1 | B18 |
| 40 | D2 | D18 |
| 41 | D3 | E18 |
| 43 | D4 | F1 |
| 44 | D5 | G18 |
| 45 | D6 | J17 |
| 46 | D7 | J18 |
| 48 | RXF# | G13 |
| 52 | TXE# | K16 |
| 53 | RD# | D9 |
| 54 | WR# | M13 |
| 55 | SIWUB | D10 |
Neso Revision V2:
Header P4
In Neso Revision V1, GPIO 130 and GPIO 131 were connected to pin locations C15 and D15 respectively.
In Neso Revision V2, in pin locations, C15 and D15, FTDI OE and FTDI CLKOUT signals are connected respectively. And GPIO 130 is now connected to pin J5 in Bank 35 and GPIO 131 is connected to pin T8 in Bank 34 which is powered by 1.5V.
| Pin No. On The Header | Artix-7 (CSG324) Pin No. | Pin No. On The Header | Artix-7 (CSG324) Pin No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND | 2 | 3V3 |
| 3 | VCCIN | 4 | GND |
| 5 | A14 | 6 | A13 |
| 7 | D13 | 8 | D12 |
| 9 | A11 | 10 | B11 |
| 11 | F14 | 12 | F13 |
| 13 | B14 | 14 | B13 |
| 15 | A16 | 16 | A15 |
| 17 | A9 | 18 | A10 |
| 19 | B12 | 20 | C12 |
| 21 | A8 | 22 | B8 |
| 23 | C10 | 24 | C11 |
| 25 | B9 | 26 | C9 |
| 27 | B6 | 28 | B7 |
| 29 | C5 | 30 | C6 |
| 31 | A5 | 32 | A6 |
| 33 | C7 | 34 | D8 |
| 35 | D7 | 36 | E7 |
| 37 | D4 | 38 | D5 |
| 39 | - | 40 | - |
| 41 | - | 42 | - |
| 43 | D3 | 44 | E3 |
| 45 | - | 46 | - |
| 47 | A3 | 48 | A4 |
| 49 | GND | 50 | GND |
| 51 | GND | 52 | GND |
| 53 | - | 54 | - |
| 55 | B2 | 56 | B3 |
| 57 | C1 | 58 | C2 |
| 59 | A1 | 60 | B1 |
| 61 | G1 | 62 | H1 |
| 63 | E1 | 64 | F1 |
| 65 | - | 66 | - |
| 67 | D2 | 68 | E2 |
| 69 | K1 | 70 | K2 |
| 71 | J2 | 72 | J3 |
| 73 | B4 | 74 | C4 |
| 75 | E5 | 76 | E6 |
| 77 | G2 | 78 | H2 |
| 79 | F3 | 80 | F5 |
| 81 | G3 | 82 | G4 |
| 83 | H5 | 84 | H6 |
| 85 | H4 | 86 | J4 |
| 87 | F6 | 88 | G6 |
| 89 | GND | 90 | GND |
| 91 | GND | 92 | GND |
| 93 | 3V3 | 94 | 3V3 |
| 95 | 3V3 | 96 | 3V3 |
Header P5
| Pin No. On The Header | Artix-7 (CSG324) Pin No. | Pin No. On The Header | Artix-7 (CSG324) Pin No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BCBUS0* | 2 | BCBUS1 |
| 3 | 3V3 | 4 | GND |
| 5 | BCBUS2 | 6 | BCBUS3 |
| 7 | B16 | 8 | B17 |
| 9 | BCBUS4 | 10 | BCBUS5 |
| 11 | D14 | 12 | C14 |
| 13 | BCBUS6 | 14 | BCBUS7 |
| 15 | C16 | 16 | C17 |
| 17 | H14 | 18 | G14 |
| 19 | T8 | 20 | J5 |
| 21 | E15 | 22 | E16 |
| 23 | E17 | 24 | D17 |
| 25 | F15 | 26 | F16 |
| 27 | J14 | 28 | H15 |
| 29 | H17 | 30 | G17 |
| 31 | H16 | 32 | G16 |
| 33 | K13 | 34 | J13 |
| 35 | L15 | 36 | L16 |
| 37 | L18 | 38 | M18 |
| 39 | R12 | 40 | R13 |
| 41 | K15 | 42 | J15 |
| 43 | M16 | 44 | M17 |
| 45 | GND | 46 | GND |
| 47 | GND | 48 | GND |
| 49 | GND | 50 | GND |
| 51 | GND | 52 | GND |
| 53 | R18 | 54 | T18 |
| 55 | P15 | 56 | R15 |
| 57 | N15 | 58 | N16 |
| 59 | N14 | 60 | P14 |
| 61 | P17 | 62 | R17 |
| 63 | N17 | 64 | P18 |
| 65 | U16 | 66 | V17 |
| 67 | U17 | 68 | U18 |
| 69 | U14 | 70 | V14 |
| 71 | V15 | 72 | V16 |
| 73 | T14 | 74 | T15 |
| 75 | R16 | 76 | T16 |
| 77 | T9 | 78 | T10 |
| 79 | T13 | 80 | U13 |
| 81 | T11 | 82 | U11 |
| 83 | R10 | 84 | R11 |
| 85 | V10 | 86 | V11 |
| 87 | U12 | 88 | V12 |
| 89 | INITB | 90 | 3V3 |
| 91 | PROGB | 92 | 3V3 |
| 93 | GND | 94 | GND |
| 95 | GND | 96 | GND |
FT2232H – Artix-7 (CSG324) FPGA Connection Details
| FTDI Pin No. | Pin Function (245 FIFO) | Artix-7 Pin No. |
|---|---|---|
| 16 | D0 | A18 |
| 17 | D1 | B18 |
| 18 | D2 | D18 |
| 19 | D3 | E18 |
| 21 | D4 | F18 |
| 22 | D5 | G18 |
| 23 | D6 | J17 |
| 24 | D7 | J18 |
| 26 | RXF# | G13 |
| 27 | TXE# | K16 |
| 28 | RD# | D9 |
| 29 | WR# | M13 |
| 30 | SIWUA | D10 |
| 32 | CLKOUT | D15 |
| 33 | OE# | C15 |
Driver Installation
Installing on Windows
This product requires Numato Lab drivers to be installed for proper functioning when used with Windows. The driver can be downloaded from https://numato.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/Driver.zip. Windows users should download and run the WHQL Certified executable file that will prompt them to install the Numato Lab drivers.
Neso Revision V1:
| Neso USB Vendor ID | 0403 |
| Neso USB Product ID | 6010 |
Neso Revision V2:
| Neso USB Vendor ID | 2A19 |
| Neso USB Product ID | 1005 |
Note: In the revision V1 of Neso, FT2232H Channel A is dedicated to SPI Flash /JTAG Programming. Channel B can be used for custom applications. The revision V2 of Neso ships with FT2232H Channel B dedicated for SPI Flash /JTAG Programming whereas Channel A can be used for custom applications.
Installing on Linux
The Linux ships with the drivers required for Neso. It should be enough to run the following two commands in the terminal:
>> sudo modprobe stdi_sio >> echo 2a19 1005 > /sys/bus/usb-serial/drivers/ftdi_sio/new_id
Powering Up Neso
Neso is factory configured to be powered directly from the USB port so make sure that you are using a USB port that can power the board properly. It is recommended to connect the board directly to the PC instead of using a hub. It is practically very difficult to estimate the power consumption of the board, as it depends heavily on your design and the clock used. Xilinx provides tools to estimate power consumption. In any case, if power from USB is not enough for your application, external supply can be applied to the board. Jumper PWRSEL should be set up properly (short pin 1-2) to use the board on external power. Neso requires three different voltages, a 3.3V, a 1.8V supply, and a 1.3V supply. Onboard regulators derive these voltages from the USB/Ext power supply.
Generating Bit Stream for Neso
The bitstream can be generated for Neso in Vivado by following the steps below:
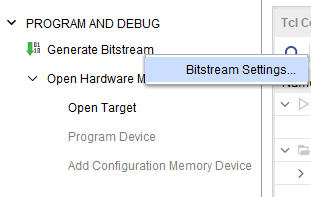
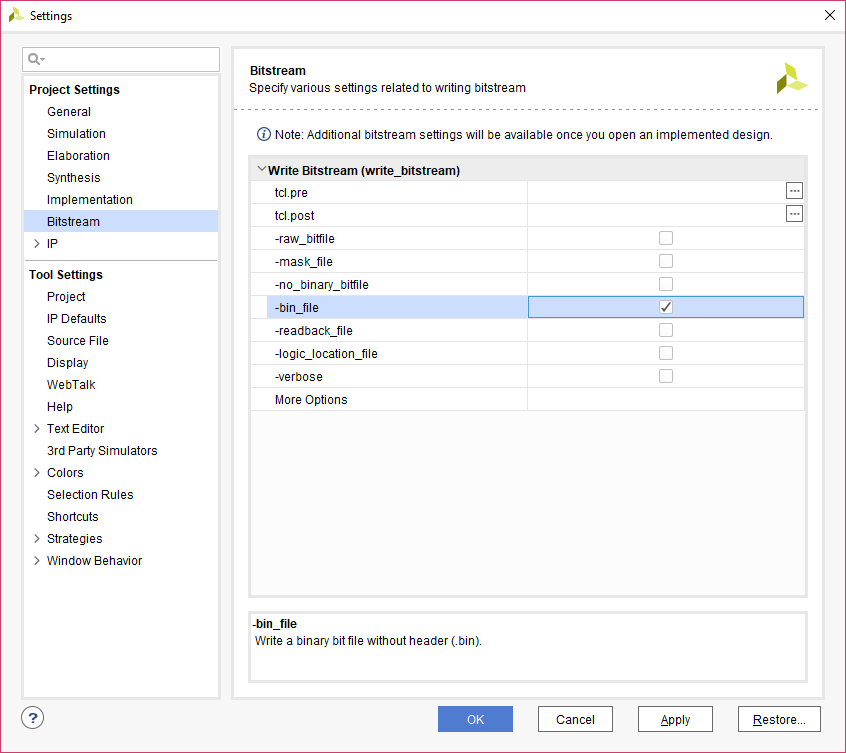
Step 1: It is recommended to generate .bin file along with .bit file. Right-click on “Generate Bitstream” under the “Program and Debug” section of the Flow Navigator window and click “Bitstream Settings”.
Step 2: Select “-bin_file” option in the dialog window and click “Apply” and then “OK”.
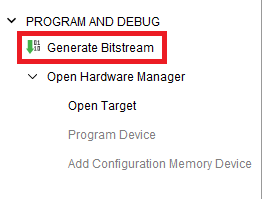
Step 3: Finally click “Generate Bitstream”.
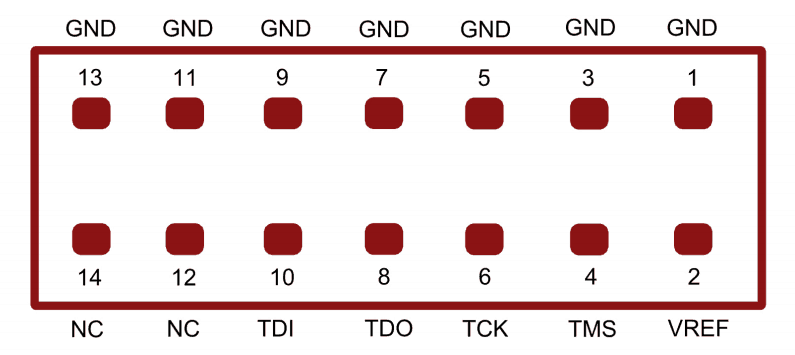
Programming Neso Using JTAG
Neso Artix 7 FPGA Development Board features an onboard JTAG connector which facilitates easy reprogramming of SRAM and onboard SPI flash through JTAG programmer like “Xilinx Platform cable USB”. Following steps illustrate how to program FPGA on Neso using JTAG.
Step 1: By using JTAG cable, connect Xilinx platform cable USB to Neso and power it up.
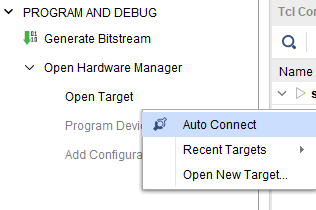
Step 2: Open Vivado project and open the target by clicking on the “Open Target” in “Open Hardware Manager” in the “Program and Debug” section of the Flow Navigator window. Select “Auto Connect”.
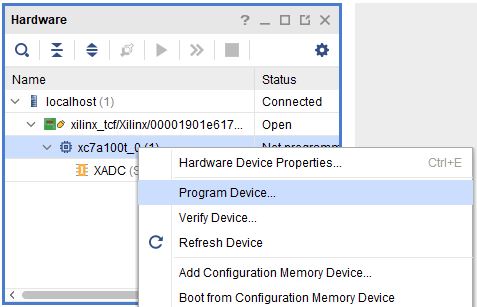
Step 3: If the device is detected successfully, then select “Program Device” after right clicking on the target device “xc7a100t_0 (1)” as shown below.
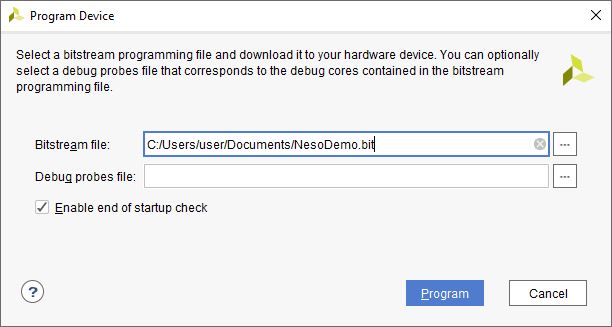
Step 4: In the dialog window which opens up, Vivado automatically chooses correct bitstream file if the design was synthesized, implemented and bitstream generated successfully. If needed, browse to the bitstream which needs to be programmed to FPGA. Finally, click “Program”.
Programming QSPI Flash using Vivado
A .bin or .mcs file is required for programming Neso Artix 7’s onboard QSPI flash.
Step 1: Open Vivado Project. Click on “Open Target” in “Open Hardware Manager” in the “Program and Debug” section of the Flow Navigator window.
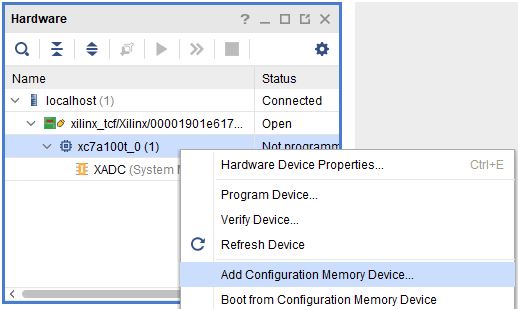
Step 2: If the device is successfully detected, then right-click on the “xc7a100t_0 (1)”. Select “Add Configuration Memory Device” as shown below.
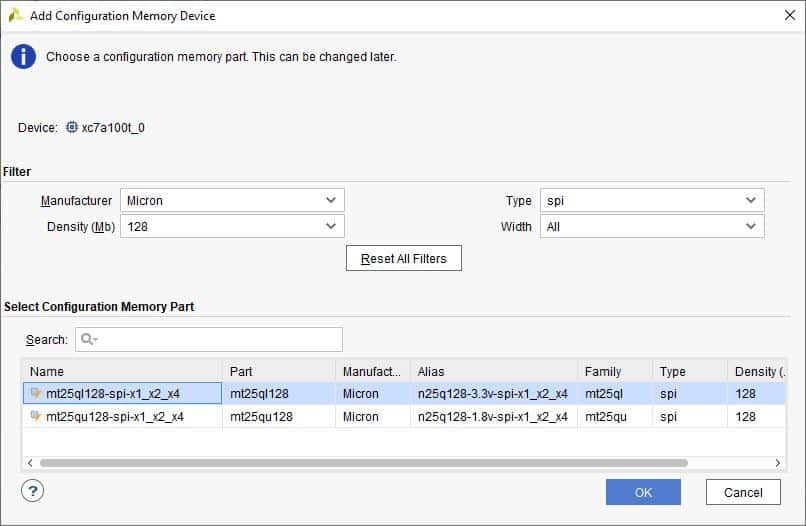
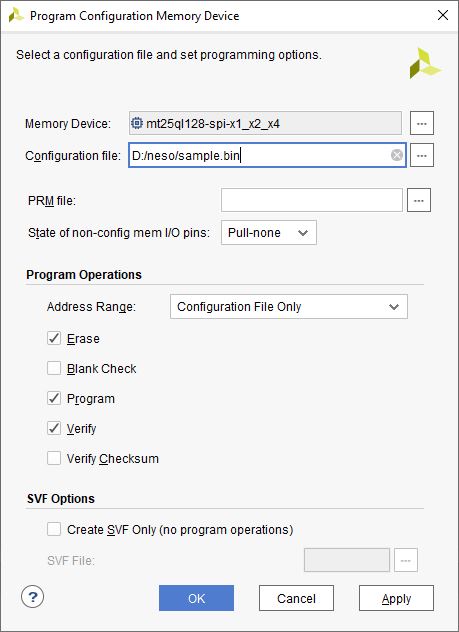
Step 3: Select the memory device “mt25ql128-spi-x1_x2_x4 (which is equivalent to n25q128-3.3v-spi-x1_x2_x4)”, then click OK.
Step 4: After completion of Step 3, a dialog box will open. Click OK.
Step 5: Browse to the working .bin file or the .mcs file (whichever applicable) and click OK to program as shown below. If programming is successful, a confirmation message will be displayed.
Programming Neso Using Tenagra
For steps on how to program Neso using Tenagra, refer the Getting started with Tenagra FPGA System Management Software article.
Technical Specifications
| Parameter * | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Specifications | ||
| Number of GPIOs | 148(Max) | |
| On-board oscillator frequency (FXO-HC536R) | 100 | MHz |
| DDR3 Capacity | 2 | Gb |
| SPI Flash Memory (N25Q128A13ESE40E) | 128 | Mb |
| Power supply voltage (USB or external) | 5 – 6 | V |
| FPGA Specifications | ||
| Internal supply voltage relative to GND | –0.5 to 1.1 | V |
| Auxiliary supply voltage relative to GND | –0.5 to 2.0 | V |
| Output drivers supply voltage relative to GND | –0.5 to 3.6 | V |
Neso GPIO Easy Reference
Neso Revision V1: Neso GPIO Easy Reference
Neso Revision V2: Neso GPIO Easy Reference