Introduction
Numato Lab’s 4-Channel USB Reed Relay Module offers a streamlined and effective solution for remotely managing electrical and electronic devices via USB from either a PC or mobile device. Engineered for user convenience and broad compatibility across operating systems, this module integrates a USB to serial converter, eliminating the need for specialized USB expertise. Users can easily operate the module through standard terminal emulation software, such as HyperTerminal and PuTTY, using straightforward, human-readable commands. For advanced applications, custom control programs can be developed in various programming languages, providing flexibility for developers and engineers. This module features four high-quality reed relays, offering key benefits such as compact size, rapid switching, which ensure enhanced reliability and longevity. The reed relays are ideal for switching low-power signals in a variety of applications, including automated testing, remote control, and data acquisition systems. Powered directly from the USB port, the module is both user-friendly and energy-efficient, making it a versatile and reliable choice for a wide range of applications.
Features
- 4 Reed Relays: Supports contact ratings up to 200V, 0.5A DC / 140V, 0.35A AC
- 8 TTL-Compatible GPIOs: 5V logic level, suitable for interfacing with various digital devices.
- : Multiplexed with GPIOs, providing versatile input options.
- 10-Bit Analog Input Resolution: Offers precise analog-to-digital conversion for accurate measurements.
- USB Interface with CDC Support: Operates like a standard serial port, requiring no specialized USB knowledge.
- Accessible Relay Contacts: Relay contacts are available via convenient screw terminals for easy integration.
- USB-Powered Digital Circuitry: The module’s digital circuitry is powered directly from the USB connection, simplifying power management.
- Versatile Control Options: Can be controlled using standard serial console applications or through custom applications, with no need for vendor-specific libraries or APIs.
Some of the possible uses of this module include
- Home Automation: Reed relays can control low-power devices such as lights, alarms, or small appliances, making them suitable for home automation systems.
- Industrial Automation: While reed relays can handle certain automation tasks, such as signal switching or controlling small loads, they might not be ideal for high-power industrial applications due to their limited current capacity.
- Lighting Control: Reed relays can efficiently switch lighting circuits, especially in low-power or LED lighting systems.
- Garden Equipment Control: They can control low-power garden equipment like irrigation systems or garden lighting, but may not be suitable for higher-powered equipment like large pumps.
- Test Fixtures: Reed relays are commonly used in test fixtures for signal switching, due to their fast response and reliability.
- DIY and Hobby: Ideal for DIY projects and hobbies, reed relays are easy to use for controlling small circuits and devices.
This product is compatible with the following operating systems:
- Windows XP and later versions (Windows 7, 8/8.1, 10 and future versions)
- Windows 7 Embedded and later
- Linux
- Mac OS X
- Android
- Or any other operating system that supports USB CDC devices.
And these are some of the languages that can be used for programming:
- C/C++
- Visual Basic (VB6, VB2008, VB2010 express and other editions)
- Visual Basic for Applications (Microsoft Office VBA)
- Perl
- Python
- JAVA
- Android
- Javascript (Node.js)
- And many more…
A complete list of sample code is available here.
This product has four onboard reed relays and associated drivers capable of controlling a variety of devices including lamps, motors, locks etc… (Please see recommendations for using this product with inductive loads elsewhere in this document). This module also includes General Purpose I/Os, and analog inputs (multiplexed with GPIOs) that can be accessed over USB interface for extended functionality. The module communicates with host PC over full-speed USB link. When connected to PC, the module will appear as a serial port in Windows Device Manager (or a serial tty device in Linux and Mac).
How to Use 4 Channel USB Reed Relay Module
Using this product is very easy, thanks to the human-readable and easy to use command set and the USB CDC interface that allows the device to be used with most readily available serial terminal software such as Tera Term or HyperTerminal. This document has more information about using this device with the following Serial terminal software. But in no way limited to this software though.
- Windows
- HyperTerminal
- Putty
- Tera Term
- Linux
- GNU Screen
- PuTTY
- Mac OS X
- Screen Command
- CoolTerm
- goSerial
Using this product involves the following simple steps.
- Connect the device to a USB port on the host system
- Install driver (Only needed for Windows. Driver available for download on the product page.)
- Open the COM port corresponding to the device using a Serial Terminal software
- Enter commands (Very similar to entering commands at DOS prompt or Bash prompt)
- Optionally write a script or application to automate your task (More info on custom programming/scripting is available in this document. Also we have a large set of sample code to help you with)
All aspects of the above steps are covered in the following sections including step by step demonstration.
Components/Tools Required
Along with the module, you may need the items in the list below for easy and fast installation.
1. USB A to C cable.
2. Medium size Philips screw driver.
USB Interface
The on board full speed USB controller helps a PC/Linux/computer to communicate and control this module seamlessly. Use a USB A to C cable to connect with a PC. Please visit http://www.numato.com to buy cables and accessories for this product. By default, the logic section of the module is powered from USB so make sure not to overcrowd unpowered USB hubs
Relay Contacts
This module has four reed relays that can switch up to 0.5A DC and 0.35A AC current. All contacts on the relay is available externally on screw terminals for easy user access. The relays are rated for AC and DC supply voltages. Please see the technical specification table for more details. Each relay has 2 contacts(COM, NO). The contacts COM and NO will be disconnected when relay is turned off and will be connected when the relay is turned on.
GPIO/Analog Inputs
In addition to the onboard relay, this module has 8 General Purpose IO pins that can be used for various custom applications. Six of these pins can be used as Analog to Digital Converter inputs as well. All IO pins support 5V TTL signals and the ADC input range is 0 to +5V. The ADC can acquire analog signal at the resolution of 10 bits per sample. It is recommended to use a series resistor with the GPIO/ADC pins when interfacing with other circuits. In output mode, GPIOs can source up to 25mA. So no additional circuitry is needed to drive regular LEDs. A 470 Ohms series resistor is recommended for current limiting when connecting LED to a GPIO.
In contrast to GPIOs, Analog inputs can read voltages at any level between 0 to 5V. It is recommended to use a series resistor to protect the input from stray voltages and spikes. The internal Analog to Digital converter supports 10 bits resolution which is adequate for most applications. The table below summarizes the GPIO and Analog to Digital Converter input positions on the header.
| GPIO | ADC |
|---|---|
| IO0 | ADC0 |
| IO1 | ADC1 |
| IO2 | ADC2 |
| IO3 | ADC3 |
| IO4 | NA |
| IO5 | NA |
| IO6 | ADC4 |
| IO7 | ADC5 |
| GND | GND |
| +5V | VDD |
DC Power Supply
This module uses +5V power supply to function properly. By default the board is configured to use +5V supply from USB. So an external +5V power is not required. In most cases USB ports are capable of providing enough current for the module. Please refer to the marking on the board for more details.
Driver Installation
Installing Numato Lab CDC Driver - Windows Desktop and Server Editions
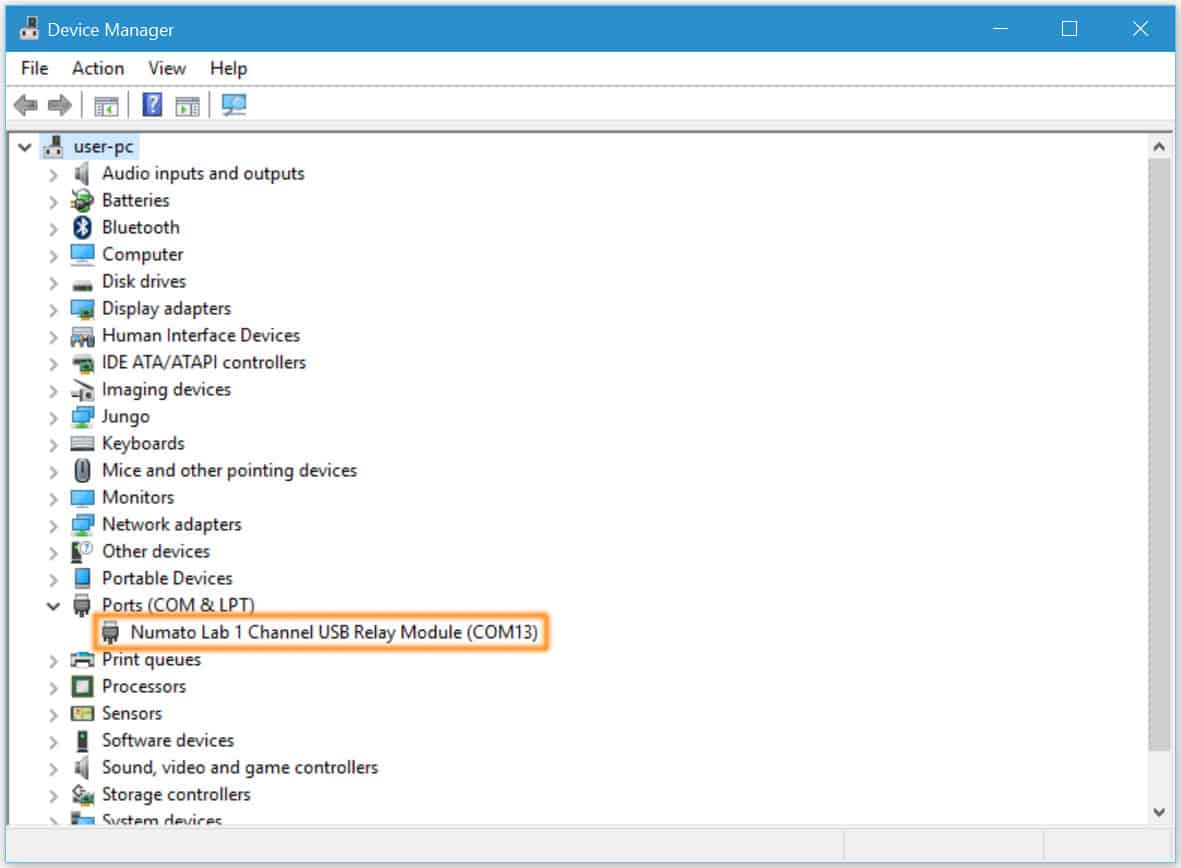
The driver package for Numato Lab’s products can be downloaded from the product page at ttp://numato.com. To install the driver, unzip the contents of the downloaded driver package to a folder. Attach USB cable to the PC and when asked by Windows device installation wizard, point to the folder where driver files are present. When driver installation is complete, the module should appear in Windows Device Manager as a serial port. The picture below shows a 1 Channel USB Relay Module visible in Windows Device Manager. For other devices (USB GPIO and USB Relay modules), the name will be different but how the device is displayed and used is exactly same.
Note down the name of the serial port (COM1, COM2 etc..). This information is required to control the module from the PC.
You may notice that the driver package does not come with a .sys or .exe file as most driver packages do and is expected to be that way. The driver binary necessary in this case is shipped with all copies of windows Desktop/Server editions and gets installed automatically while Windows is installed for the first time. The .inf and .cat files present in the driver package downloaded from http://numato.com merely associate this pre-existing driver with the attached Numato Lab device .
The following video demonstrates how to install the driver on Windows 10.
Installing on Windows Embedded Editions
Windows Embedded editions do not install the infrastructure necessary for USB CDC by default in favor of a smaller footprint. This will cause the driver install to fail unless the necessary files are manually installed prior to installing the driver. Please follow the steps below to install the prerequisites and driver correctly. These steps are tested on Windows 7 Embedded Edition.
- Locate winemb-inf-mdmcpq.cab on Win 7 Embedded DVD/ISO image
- Copy winemb-inf-mdmcpq.cab to a folder Ex: C:Temp
- Run command DISM.exe /online /Add-Package /PackagePath:C:Temp
- Wait for Windows to restart (Restart machine manually if DISM does not restart the machine automatically)
- After reboot is complete, plug the device to a USB port and install driver normally (Driver is available for download at the product page)
Installing on Linux
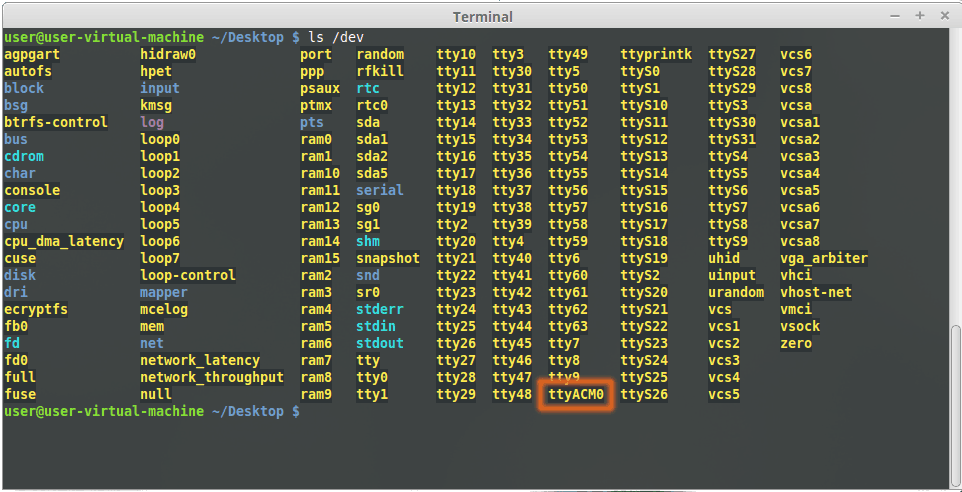
To use any device that uses USB CDC protocol with Linux, USB CDC driver needs to be compiled in to the kernel. Fortunately, most Linux distributions (Ubuntu, Redhat, Debian etc..) has this driver pre-installed. The chances of you requiring to rebuild the kernel to include the USB CDC driver is very slim. When connected to a Linux machine, this product should appear as a serial port under /dev directory. Usually the name of the device will be ttyACMx or similar. The name may be different depending on the Linux distribution you have. The image below shows the result of ls /dev command on a Linux Mint system with a USB GPIO/Relay device attached.
In this particular case, the device shows up as ttyACM0 (highlighted in orange color) but it could be ttyACM1 or ttyACM2 etc… depending on the specific system and other connected devices. Once the device is visible under /dev directory, it can be treated just like any other serial device. Commands can be sent to the device using any mechanism that is valid for regular serial ports such as screen command or Serial Terminal Emulation applications. If there are more than one devices connected to the same host computer, each device will be displayed as separate serial devices with unique names. These separate serial devices can be used to control individual devices attached.
Installing on Mac OSX
Mac OSX is usually shipped with USB CDC driver pre-installed. When connected to a Mac computer, this product should appear as a serial port under /dev directory. Usually the name of the device will be tty.usbserialportx or similar. The name may be different depending on the Mac OSX version you have. The image below shows the result of ls /dev/*usb* command on a Mac OSX Yosemite system with a USB GPIO/Relay device attached.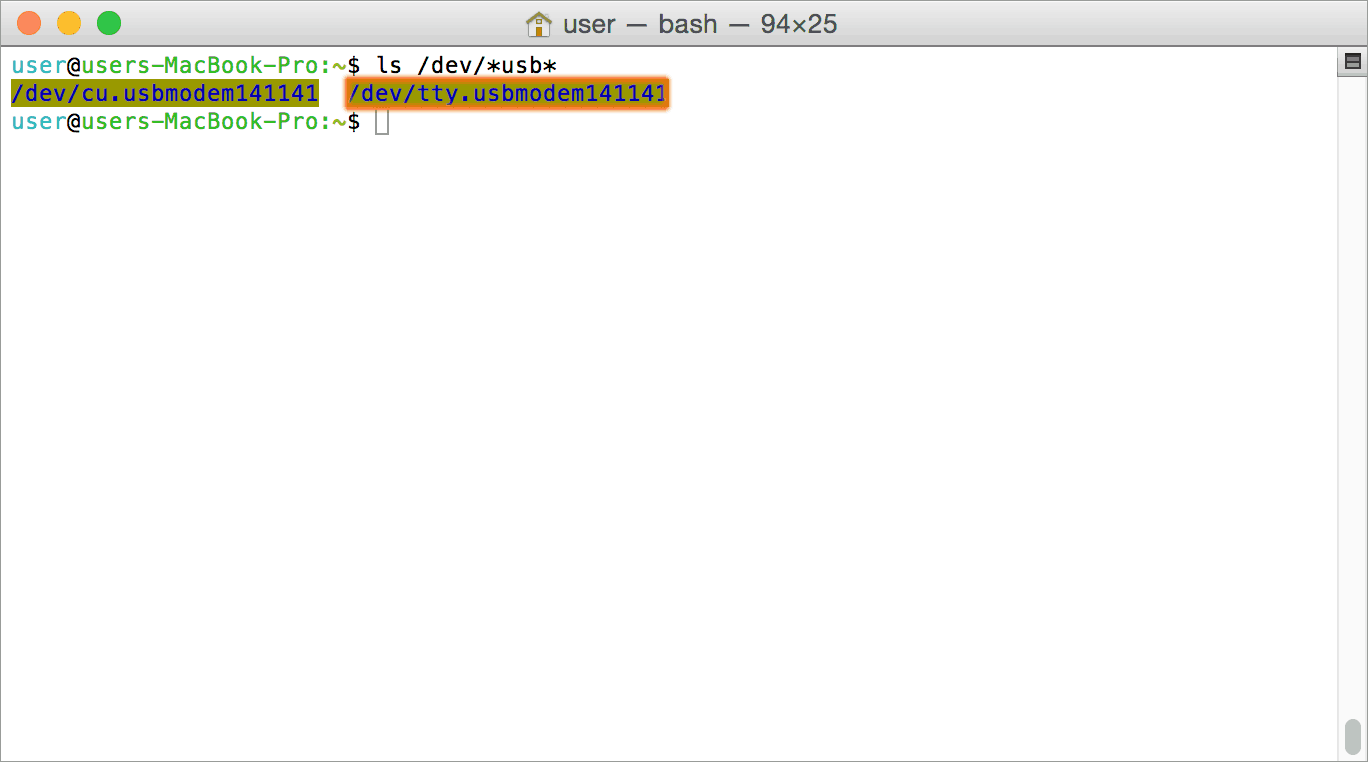
In this particular case, the device shows up as tty.usbmodem141141 (highlighted on orange color) but it could be any name starting tty.usbmodem or even a completely different name depending on the exact version of operating system and other connected devices. Once the device is visible under /dev directory, it can be treated just like any other serial device. Commands can be sent to the device using any mechanism that is valid for regular serial ports such as screen command or Serial Terminal Emulation applications. If there are more than one devices connected to the same host computer, each device will be displayed as separate serial devices with unique names. These separate serial devices can be used to control individual devices attached.
Installing CDC Devices On Android
Most Android versions has built in driver that supports external USB Devices. Due to the presence of built-in driver any external USB device including Numato Lab’s USB GPIO/Relay products connected to Android based gadget will be enumerated by Android OS. Such enumerated devices can be listed/viewed by using apps such as USB Device Info. The image below shows info about a Numato Lab USB device printed by USB Device Info app. All Numato Lab’s USB GPIO and USB Relay modules will be displayed the same way.
Devices detected by Android can be controlled by using any off the shelf Serial Terminal App such as USB Serial Terminal Lite.
Sending Commands
One of the most powerful features of this module is the simple easy to use command set it supports. This command set hides the complex USB protocol and gives a very simple interface to access the features of the module. The following sections give details of the command set and how to use the command set.
The Command Set
This product supports a very simple command set that is designed to be less cryptic and easy to use manually (using serial terminal emulation programs) or through a program written in many supported languages.
List of currently supported commands.
| No. | Command | Parameters | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ver | none | ver | Returns firmware Version. |
| 2 | id | get/set xxxxxxxx | id get, id set 12345678 | Reads/Writes ID of the module |
| 3 | relay | on/off/read, relay number readall/writeall/poweron | relay on 000, relay off 000, relay read 000, relay readall/ relay writeall 0f, relay poweron 0f | Control the relays |
| 4 | reset | none | reset | resets all the relays to the off condition |
| 5 | gpio | set/clear/read/status, gpio number, poweron | gpio set 000, gpio clear 000, gpio read 000, gpio status 000, gpio poweron 00 ff | Control General Purpose Input/Output |
| 6 | adc | read | adc read 000 | Read Analog to Digital Converter input |
| 7 | info | none | info | Returns Relay Power-On status, GPIO Power-On Direction & Status |
The table below has more detailed information about available commands.
| No. | Command | Example | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ver | ver | Returns current firmware version. |
| 2 | id | id get id set xxxxxxxx | Id get reads the module ID. Id set will assign a new ID to the module. “x” stands for alphanumeric characters including symbols. The new ID must be exactly 8 characters in length. |
| 3 | relay | relay on xxx | Turns a particular relay on. The parameter “xxx“ stands for the relay number. The relay number starts from 000. See some examples below. relay on 000 – Turns on relay 0 relay on 001 – Turns on relay 1 This command accepts RELAY number from 000 – 003, total 4 values for 4 Channel USB Reed Relay Modules. |
| relay off xxx | Turns a particular relay off. The parameter “xxx“ stands for the relay number. The relay number starts from zero. See some examples below. relay off 000 – Turns off relay 0 relay off 001 - Turns off relay 1 This command accepts RELAY number from 000 – 003, total 4 values for 4 Channel USB Reed Relay Modules. |
||
| relay read xxx | Returns the status of a particular relay. The parameter “xxx“ stands for the relay number. The relay number starts from zero. See some examples below. relay read 000 - Returns status of relay 0 relay read 001- Returns the status of relay 1 The data returned in response to this command will be either “on” or “off” depending on the current status of the relay. This command accepts RELAY number from 000 – 003, total 4 values for 4 Channel USB Reed Relay Modules |
||
| relay readall | Reads the status of all relays in a single operation. The return value will be a hexadecimal number with binary value 1 at bit positions for relays in ON state and 0 for relays in OFF state. Eg: a return value 00 (binary 0000 0000) means all relays are OFF. A value 0F (binary 0000 1111) means all relays are ON. relay readall – Returns status of all relays Refer Understanding readall/writeall commands for Relay Modules to know more. |
||
| relay writeall 0x | Control all relays in a single operation. A hexadecimal value must be specified with desired bit positions set to 0 or 1. A value 0 at a bit position will turn off the corresponding relay. A value 1 at a bit position will turn on the corresponding relay. relay writeall 0f – Turns on all relays Refer Understanding readall/writeall commands for Relay Modules to know more. |
||
| relay poweron 0x | This command is to control the relay status in a single operation. Eg. relay poweron 0c Relays 0 and 1 are in off state and relays 2 and 3 are in on state after the poweron. |
||
| 4 | reset | resets all the relays to the off condition | |
| 5 | gpio | gpio set xxx | Sets the GPIO output status to high. Here “xxx” is the number of the GPIO. This command accepts GPIO number from 000 - 007, total 8 values Please see examples below. gpio set 000 – Sets GPIO 0 to high state gpio set 004 – Sets GPIO 4 to high state |
| gpio clear xxx | Sets the GPIO output status to low. Here “xxx” is the number of the GPIO. This command accepts GPIO number from 000 - 007, total 8 values. Please see examples below. gpio clear 000 – Sets GPIO 0 to low state gpio clear 003 – Sets GPIO 3 to low state |
||
| gpio read xxx | Reads the digital status present at the input mentioned. Here “xxx” stands for the number of GPIO. This command accepts GPIO number from 000 - 007, total 8 values. The response will be either “on” or “off” depending on the current digital state of the GPIO. Please see examples below. gpio read 000 – Reads GPIO 0 status gpio read 004 – Reads GPIO 4 status |
||
| gpio status xxx | Reads the GPIO status present at ‘xxx’ without changing the GPIO to inputs. gpio status 007 – Read status of IO7 and print either ‘1’ or ‘0’ depending on the status xxx = 000 to 031 |
||
| gpio poweron xx xx | This command is to control Power-On GPIO Direction and status in a single operation. gpio poweron 00 ff – Sets GPIOs IO direction and status respectively at each bit position according to the bits of the specified hexadecimal value. IO direction: 0 – To set the GPIO as output mode & 1 – To set the GPIO as input mode. IO status: 0 - To clear the GPIO & 1 - To set the GPIO. ‘f0 ff’- (1111 0000 ) (1111 1111): GPIOs 0 - 3 are set to output mode & GPIOs - 4 to 7 are set as input mode. GPIO 0 - 7 are set to High. |
||
| 6 | adc | adc read xxx | Reads the analog voltage present at the ADC input mentioned. “x” stands for the number of ADC input. The response will be a number that ranges from 0 – 1023. Please see examples below. adc read 000 – Reads analog input 0 adc read 004 – Reads analog input 4 |
| 7 | info | Returns Relays Power-On Status, GPIO Power-On Direction & Status. |
Accessing the module
4 Channel USB Reed Relay (DPST) Module allows to communicate through any of the Serial Terminal Emulator Software
using simple easy to use commands mentioned in the command set above.
Refer documentation “Sending Commands to the Numato Lab USB Modules” to know more.
Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Number of relays | 4 | |
| Number of GPIOs | 8 | |
| Number of analog inputs (Multiplexed with GPIOs) | 6 | |
| Digital circuit power supply voltage | 5 | V |
| Maximum current drawn by digital circuitry | 10 | mA |
| IO Specifications | ||
| Maximum IO source current | 25 | mA |
| Maximum IO sink current | 25 | mA |
| GPIO input low voltage | 0.8 | V |
| GPIO input high voltage | 2 | V |
| GPIO output low voltage | 0 | V |
| GPIO output high voltage | 5 | V |
| ADC Specifications | ||
| Resolution | 10 | bits |
| Full scale range | 0 – VDD | V |
| Reference voltage | VDD | V |
| Recommended Impedance of Analog Voltage Source | 2.5 | KΩ |
| Relay Specifications | ||
| Nominal relay coil voltage | 5 | V |
| Contact rating | 200V 0.5A DC/ 140V 0.35A AC | |
| Maximum switching voltage | 200Vdc/ 140Vac | V |
| Maximum switching current | 0.5Adc/ 0.35Aac | A |
| Maximum switching power | 10 | W |
| Contact resistance (initial) | 0.150 | Ω Max. |
| Nominal insulation resistance | 10000 | MΩ Min |
| Nominal switching on response time | 1.0 | ms |
| Other Information | ||
| USB Vendor ID | 0x2A19 | |
| USB Product ID | 0x0C1A | |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q. What are the serial parameters I need to use when communicating with this board?
A. Since this module uses USB as the underlying transport mechanism, most of the serial parameters do not affect the communication. You can leave all parameters to any legal value (Eg: 2400, 4800, 9600 etc… for baud rate) except Flow control. Flow control needs to be set to “None”.
Q. Where do I find driver for this product?
A. Visit http://numato.com and navigate to the product page. There will be a link to download windows driver. Linux does not require driver installation since in most cases they are shipped with the driver pre-installed.
Q. Why there is no .sys or .exe file in the Windows driver package I downloaded?
A. This product uses USB CDC driver binary which is already present on Windows. All Windows versions (with the exception of Embedded Editions) has this driver binary installed by default. The .inf and .cat files present in the zip file helps Windows identify the device properly and associate appropriate driver (.sys) to the device
Q. Does this product work with Linux?
A. Yes, this product works with Linux. Please see more details on how to use this product with Linux elsewhere in this document.
Q. Does this product work with Mac OSX?
A. Yes, this product works with Mac OSX. Please see more details on how to use this product with Mac elsewhere in this document.
Q. What are the serial terminal software that this product work with?
A. This product works with a lot of different Serial Terminal software. Some examples can be found elsewhere in this document. Different Serial Terminal software are written by different developers with different purposes in mind. So you may encounter some software that may not work with this product. But usually alternatives are available in most if not all cases.
Q. The GPIO looses its previously set value when trying to read the status. Why it is so?
A. When a gpio is to output a value (high/low), that particular GPIO is put to output mode. When you are trying to read the GPIO, it needs to be put in input mode. In input mode, the GPIO will go to high impedance state and thus looses the previously set value.
Q. I’m using x language for programming. How do I find out if this language can be used to program and control the GPIO module?
A. Find out if the language of interest supports some kind of APIs/Functions/Components for serial communication. If it does, most likely you should be able to use that language with this module.
Q. What is the connector marked as ICSP on this module?
A. This connector is used to program the on-board microcontroller. This connector is primarily intended for factory use.
Q. I need a customized version of this product, can Numato do the customization for me?
A. Yes, we can definitely do customization but there may be minimum order requirements depending on the level of customization required. Please write to [email protected] for a quote.
Q. Where can I buy this product?
A. All Numato products can be ordered directly from our web store http://www.numato.com. We accept major credit cards and Paypal and ship to almost all countries with a few exceptions. We do have distributors in many countries where you can place your order. Please find the current list of distributors at http://numato.com/distrib.